第03篇_Spring_Core
第00章_前言
Spring是Java EE编程领域的一个轻量级开源框架,最早由Rod Johnson在 2002 年提出并随后创建,是为了解决企业级编程开发中的复杂性,实现敏捷开发的应用型框架 。框架的构成如下图所示,核心的模块有控制反转容器、面向切面编程、Web开发支持等。

Spring与传统的EJB相比,具有下面一些优势。
IOC支持:提供IOC容器,可以将对象间的依赖关系交由Spring进行控制,避免硬编码所造成的过度程序耦合。
AOP支持:使用面向切面编程可以十分方便的解决一些传统OOP非常棘手的问题。
事务支持:使用声明式事务方式灵活的进行事务的管理, 提高开发效率和质量。
拥抱开源:提供了各种优秀框架和第三方库的集成和封装,降低其使用难度。
轻量且高效:Spring的 jar 包非常小,且运行时占用资源少,运行效率高。
第01章_IOC容器
第一节 程序中的耦合
1. 程序中的耦合
程序中的耦合指的是代码之间的相互依赖关系。如下面一段代码,业务层需要调用持久层进行保存操作,此时业务层就对持久层产生了直接依赖,如果需要对持久层实现类进行替换,需要修改业务层代码,不符合开闭原则。
1public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {2 3 public void saveAccount() {4 // 业务层在此处直接依赖了持久层的实现类5 AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl(); 6 accountDao.saveAccount();7 }8}
2. 使用工厂模式来解决耦合
首先将持久层对象的创建交给一个工厂类来实现,那么依赖关系将由服务层->持久层转变为服务层->工厂类。然后在工厂类通过反射来创建我们所需的对象,并且可以将全类名放置在外部配置文件中,以此来解决代码中存在的直接依赖关系。
271// 1. 定义一个通用工厂,从配置文件读取全类名,并通过反射创建对象2public class BeanFactory{3 private static Properties env = new Properties();4 5 // 加载配置文件中的类名信息:key = accountDao value = org.example.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl6 static{7 try {8 InputStream inputStream = BeanFactory.class.getResourceAsStream("/beans.properties");9 env.load(inputStream);10 inputStream.close();11 } catch (IOException e) {12 e.printStackTrace();13 }14 }15 16 // 从通用工厂构造对象17 public static Object getBean(String key){18 Object ret = null;19 try {20 Class clazz = Class.forName(env.getProperty(key));21 ret = clazz.newInstance();22 } catch (Exception e) {23 e.printStackTrace();24 }25 return ret;26 }27}81// 2. 服务层通过 key 从工厂获取所需依赖2public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {3 4 public void saveAccount() {5 AccountDao accountDao = BeanFactory.getBean(“accountDao”);6 accountDao.saveAccount();7 }8}现在对持久层实现类进行动态替换时,只需要修改外部配置文件就可以了,上述这种将业务层对持久层的依赖转移给工厂的解决思路,被称为控制反转(Inversion of Control)。
控制反转是一个概念,是一种思想,指将传统上由程序代码直接操控的对象调用权交给容器,通过容器来实现对象的装配和管理。控制反转就是对象控制权的转移,从程序代码本身反转到了外部容器,通过容器实现对象的创建,属性赋值,依赖的管理。
3. 使用Spring解决程序耦合
程序中的耦合是一个普遍存在问题,我们没必要为每一个应用都重复的编写上述类似代码,业界已经提供了一个通用的,被大众所认可的优秀解决方案Spring,让我们来看看如何使用Spring来解决程序中的耦合问题。
导入Spring依赖
221 2<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>6
7 <groupId>org.example</groupId>8 <artifactId>Spring-demo01</artifactId>9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>10
11 <dependencies>12 13 <!-- 引入spring-context依赖,同时会引入spring-core、spring-beans、spring-aop、spring-expression-->14 <dependency>15 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>16 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>17 <version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version>18 </dependency>19 20 </dependencies>21 22</project>注意:一般我们会选择较新的Spring 5 版本,这需要你的JDK版本在1.8及以上,Tomcat版本在8.0及以上。
配置IOC容器
需要一个配置文件用来配置 key 和全类名的映射关系,这个文件名一般为application.xml,放在任意类路径下即可。
101 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans5http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">6
7 <!-- 配置accountDao -->8 <bean id="accountDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"/>9 10</beans>
使用IOC容器
在业务代码中通过容器来获取所需的依赖,而不是直接创建依赖对象。
101public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {2 3 public void saveAccount() {4 // 通过Spring的IOC容器来获取accountDao实现类5 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");6 AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao)ctx.getBean("accountDao");7 8 accountDao.saveAccount();9 }10}
第二节 IOC容器
1. ApplicationContext接口
ApplicationContext接口继承自 BeanFactory,代表 Spring 的 IOC 容器,容器读取配置元数据中的指令,进行对象的实例化、配置和组装。Spring为适应不同的场景,提供了多个实现类,常见的几种如下:
| 实现类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ClassPathXmlApplicationContext | 从类路径下加载配置文件,独立应用程序一般使用此种方式 |
| FileSystemXmlApplicationContext | 从磁盘位置加载配置文件,受限于操作系统,一般不常用 |
| AnnotationConfigApplicationContext | 从Java代码加载配置文件,一般适用于基于Java配置的注解开发模式 |
| XmlWebApplicationContext | 适用于Web应用的容器实现类,只有引入了web相关的依赖才能使用 |
ApplicationContext和BeanFactory的区别
BeanFactory 提供了最基本的容器功能,而 ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory 的完整超集,添加了更多的企业特定的功能。
面向切面编程(AOP)
Web应用(WebApplicationContext)
国际化(MessageSource)
事件传递(Event publication)
特别的,BeanFactory 总是会懒初始化 Bean,而 ApplicationContext 默认情况下在容器启动时初始化所有的Singleton Bean。
2. 容器的创建
容器的创建需要提供配置元数据,这些元数据可以是XML、注解或Java代码的形式。
XML配置方式
21// 加载services.xml和daos.xml中配置的元数据,创建一个Spring的IOC容器2ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
注解配置方式
21// 加载 SpringConfiguration 配置的注解创建容器2ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);SpringConfiguration 的代码如下,一般为一个配置类(@Configuration注解的类)。
71// Spring 配置类2// 1. @ComponentScan:扫描 com.itheima.Spring 包中的 spring 组件3// 2. @Import:导入其它类中的配置信息4(basePackages = "com.itheima.Spring")6({ JdbcConfig.class })7public class SpringConfiguration {}当然,也可以使用普通的组件类(@Component注解的类)或带有 JSR-330 元数据注解的类。
编程配置方式
161public static void main(String[] args) {2 // 定义一个容器(无参方式)3 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();4 5 // 注册配置类6 ctx.register(AppConfig.class, OtherConfig.class);7 ctx.register(AdditionalConfig.class);8 9 // 扫描配置类并刷新容器10 ctx.scan("com.acme");11 ctx.refresh();12 13 // 使用容器14 MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);15 myService.show();16}
3. 容器的关闭
在Web环境中,Spring 的基于 Web 的容器实现已经具有适当的代码,可以在相关 Web 应用程序关闭时正常关闭 Spring IoC 容器。在非 Web 应用程序环境中,请向 JVM 注册一个关闭钩子,这样Spring可以调用你单例 bean 上设置的 destroy 方法,以便释放所有资源。
131import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;2import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;3
4public final class Boot {5
6 public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {7 // 创建容器8 ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");9
10 // 注册关闭钩子11 ctx.registerShutdownHook(); 12 }13}JVM的关闭钩子在什么场景下有效?
答:正常退出、System.exit()、Ctrl+C中断、OutofMemory宕机、Kill pid杀死进程(kill -9除外)、系统关闭等。
3. 容器的使用
容器创建完成后,我们就可以通过使用方法T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType)检索 bean 的实例。
21// 通过key和类型检索Spring实例2PetStoreService service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreService.class);除此之外,ApplicationContext接口还有其他几种检索 bean 的方法,但是理想情况下,您的应用程序代码永远不要使用它们。
51// 通过key获取对象后,进行强制类型转换2Person person = (Person)ctx.getBean("person");3
4// 通过类型匹配获取对象(注意:此时只能有一个Bean是Person类型)5Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class);
容器除了获取对象的方法外,还提供了一些辅助方法,用于获取容器的相关信息。
141// 获取Bean总数2int count = ctx.getBeanDefinitionCount();3
4// 获取所有Bean的id5String[] beanDefinitionNames = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();6
7// 获取所有某类型Bean的id8String[] beanNamesForType = ctx.getBeanNamesForType(UserDao.class);9
10// 判断是否存在指定id的Bean(不能判断name指定的别名)11boolean isExist = ctx.containsBeanDefinition("userDao")12 13// 判断是否存在指定id的Bean(可以判断name指定的别名)14boolean isExist = ctx.containsBean("userDao")
4. 容器的扩展
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor 接口可以在 Bean 的初始化生命周期前后植入一些自定义逻辑,对创建的 Bean 进行二次加工。
281// 1. 创建一个 BeanPostProcessor2public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {3 4 /**5 * 在Bean完成实例化和注入之后、初始化之前执行6 *7 * @bean 已完成注入后的Bean对象8 * @beanName bean的id属性9 * @return 修改后的Bean对象10 */11 12 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {13 return bean;14 }15
16 /**17 * 在Bean完成初始化之后执行18 *19 * @bean 已完成初始化后的Bean对象20 * @beanName bean的id属性21 * @return 修改后的Bean对象22 */23 24 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {25 System.out.println("Bean '" + beanName + "' created : " + bean.toString());26 return categroy;27 }28}21<!-- 2. 将自定义BeanPostProcessor注册到Spring容器-->2<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="xxx.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口用于读取配置元数据,并在Bean的实例化之前对其进行修改。Spring定义了一些内置的Bean工厂后处理器,如PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer用于解析配置文件中的占位符,并进行字符串替换操作。
151<!-- 注册一个内置的BeanFactoryPostProcessor:PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 2 1. locations:指定外部属性配置文件,一般为properties格式3 2. properties:指定一些键值对形式的属性值4 3. systemPropertiesMode:是否检查System属性5 * never 从不查找System属性6 * fallback 如果从properties-ref和location中未找到需要的属性值,则去System属性查找7 * override/evironment 始终查找System属性,并覆盖其他方式配置的值8-->9<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">10 <property name="locations" value="classpath:com/something/strategy.properties"></property>11 <property name="properties" value="custom.strategy.class=com.something.DefaultStrategy"></property>12</bean>13
14<!-- 使用占位符来获取配置的属性值,这将会在Bean实例化之前进行替换-->15<bean id="serviceStrategy" class="${custom.strategy.class}"/>除此之外,与属性相关的Bean工厂后处理器还有 PropertyOverrideConfigurer,用于对配置的属性进行覆盖操作。
41<!-- 注册一个内置的BeanFactoryPostProcessor:PropertyOverrideConfigurer 2 location:指定一个外部配置文件,存放需要覆盖的属性和值,以 beanName.property=value 的格式,并支持复合属性3--> 4<context:property-override location="classpath:override.properties"/>一个 override.properties 配置文件的示例如下。
41# 覆盖 dataSource 的 driverClassName 属性值为 com.mysql.jdbc.Driver2dataSource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver3# 覆盖 tom 的 fred.bob.sammy 属性值为 1234tom.fred.bob.sammy=123
Ban(Factory)PostProcessor 的一些处理细节
Bean(Factory)PostProcessor 是容器范围的,对该容器内的所有 Bean 都生效。
Bean(Factory)PostProcessor 会尽早被实例化,即使你为它们配置了懒加载属性,容器也会忽略。
你定义了多个 Bean(Factory)PostProcessor,可以通过实现
Ordered接口并使用order属性来控制它们的执行顺序。如果你使用@Bean来创建Bean(Factory)PostProcessor,则必须保证返回类型是该接口的实现类,否则容器无法正确检测。
AOP 中一些基础结构类是基于BeanPostProcessor来实现的,因此该接口的实现类和依赖其的Bean都不适合自动代理。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 不能对实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的Bean定义进行修改。
虽然可以通过
BeanFactory.getBean()来提早实例化Bean,但这是不被推荐的,因为可以会绕过 bean 的后处理。
5. 多文件配置
引入外部配置文件
你也可以将所有元数据写在同一个配置文件中,或者通过<import/>标签引入其它文件中的元数据配置。
131<beans>2 <!-- 引入根标签为beans的外部配置文件-->3 <import resource="services.xml"/>4 <import resource="resources/messageSource.xml"/>5 <import resource="/resources/themeSource.xml"/>6 7 <!-- 使用 * 作为通配符 (注意:必须保证父配置文件名不能满足 * 所能匹配的格式,否则将出现循环递归包含)-->8 <import resource="dao/spring-*-dao.xml"/>9
10
11 <bean id="bean1" class="..."/>12 <bean id="bean2" class="..."/>13</beans>
引入外部属性文件
对于一些需要经常修改的内容,如Jdbc连接信息等,可以单独放在一个小配置文件中,方便维护。
151<!--引入外部属性文件方式一:使用PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer -->2<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">3 <property name="db-connection" value="db.properties"></property>4</bean>5
6<!-- 引入外部属性文件方法二: 要引入context命名空间-->7<!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>-->8
9<!--配置连接池-->10<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">11 <property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driverclass}"></property>12 <property name="url" value="${db.url}"></property>13 <property name="username" value="${db.username}"></property>14 <property name="password" value="${db.password}"></property>15</bean>db.properties文件示例如下:
41db.driverclass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver2db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/userDb?characterEncoding=utf-83db.username=root4db.password=root
第三节 Bean详解
1. Bean的实例化
构造方法创建
Spring配置文件的顶层标签为beans,可以配置多个<bean>标签,一个简单的bean配置示例如下:
11<bean id="accountService" class="org.example.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"/>其中id属性是全局的唯一标识,用于从容器中获取对象。class属性则是对应的全限定类名,默认情况下,使用反射调用类中的无参构造函数来创建对象,如果缺少无参构造则无法创建。
FactoryBean创建
随着业务的复杂性提升,某些复杂对象的创建不能直接通过new关键字来实现,如Connect、SqlSessionFactory等,为此Spring提供了实现FactoryBean接口的方式来完成复杂对象的配置,首先实现FactoryBean接口,示例如下。
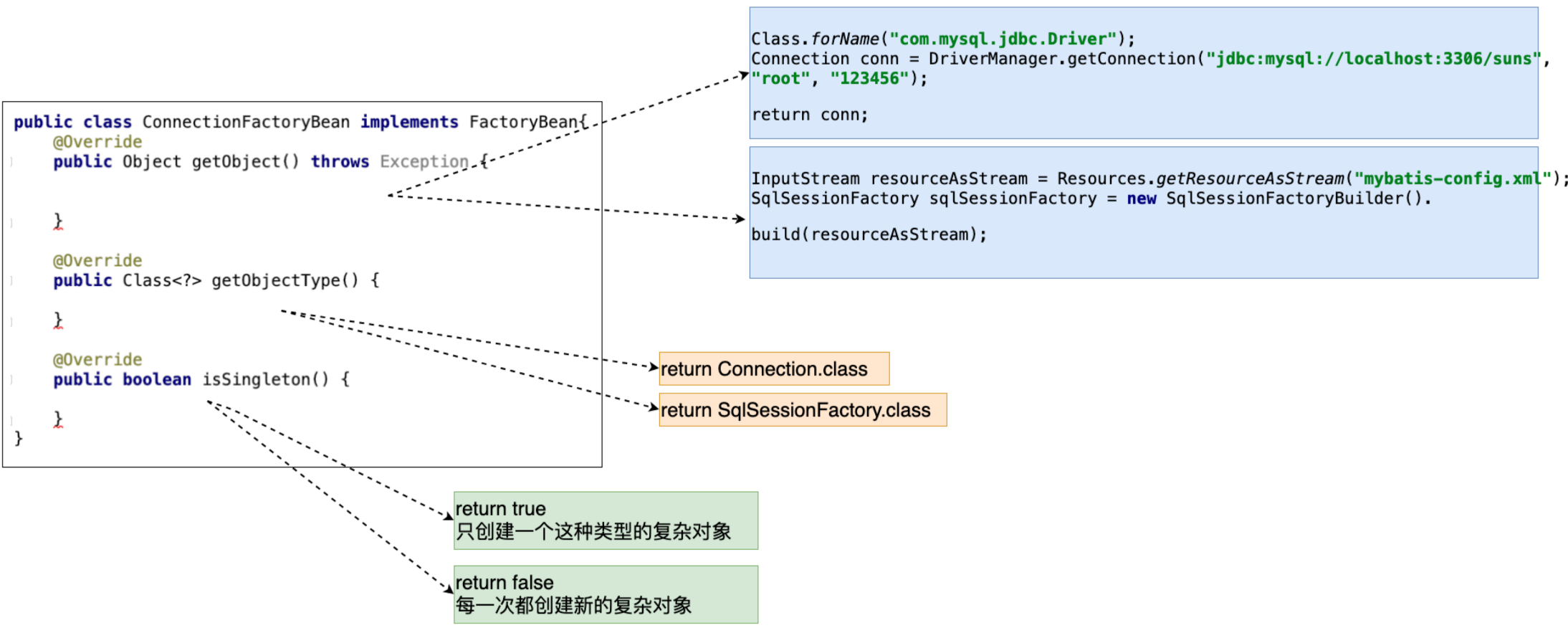
然后在配置文件中引用FactoryBean实现类来创建所需要的对象,配置如下:
11<bean id="conn" class="com.baizhiedu.factorybean.ConnectionFactoryBean"/>值得注意的是,这和简单对象的配置很相似,但实际上,Spring会检测class属性配置的类,如果是FactoryBean接口的实现类,那么通过id值获得的是这个类所创建的复杂对象(如:Connection)。
提示:就想获得FactoryBean类型的对象,可以通过
ctx.getBean("&conn")的方式获取,得到的就是ConnectionFactoryBean对象。
普通工厂类来创建
虽然上述方式解决了复杂对象创建的问题,但使用的工厂类必须实现FacotryBean接口,为了整合一些遗留系统,Spring还可以使用普通的工厂类来创建所需的对象。
工厂方法为静态方法
这种方式也是在class属性指定使用的工厂类,但需要通过factory-method属性额外指定创建对象的静态方法,示例如下:
61public class StaticFactory {2 // 创建对象的静态方法3 public static IAccountService createAccountService() {4 return new AccountServiceImpl();5 }6}21<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.factory.StaticFactory" 2 factory-method="createAccountService"></bean>
工厂方法为非静态方法
如果factory-method是非静态方法,那么将class属性留空,使用factory-bean属性引用工厂类对象,示例如下:
61public class InstanceFactory {2 // 创建对象的非静态方法3 public IAccountService createAccountService(){ 4 return new AccountServiceImpl(); 5 } 6} 111<!-- 创建工厂类对象 -->2<bean id="instancFactory" class="com.itheima.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean> 3
4<!-- 创建业务对象5 * factory-bean 属性:用于指定工厂类bean的id6 * factory-method 属性:用于指定实例工厂中创建对象的方法7-->8 <bean id="accountService" 9 factory-bean="instancFactory" 10 factory-method="createAccountService"></bean> 11
2. Bean的生命周期
生命周期指Bean从创建到销毁的整个过程,Spring提供了一些机制允许我们对bean生命周期的管理进行干预。
@PostConstruct /@PreDestroy注解
@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 是 JSR-250 的生命周期注解,Spring 在 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 中对其做了实现。在 Bean 的初始化期间会调用被@PostConstruct注解的方法,在销毁期间会调用被@PreDestroy注解的方法。
121public class CachingMovieLister {2
3 4 public void populateMovieCache() {5 // populates the movie cache upon initialization...6 }7
8 9 public void clearMovieCache() {10 // clears the movie cache upon destruction...11 }12}
InitializingBean/DisposableBean接口
如果bean实现了InitializingBean接口,容器会在创建bean的时候调用其afterPropertiesSet()方法,如果实现了DisposableBean接口,容器在销毁bean的时候调用其destroy()方法。
11<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.AnotherExampleBean"/>101public class AnotherExampleBean implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {2
3 public void afterPropertiesSet() {4 // do some initialization work5 }6
7 public void destroy() {8 // do some destruction work (like releasing pooled connections)9 }10}
init-method/destroy-method属性
对于基于 XML 的配置元数据,可以使用init-method/destroy-method属性指定无参无返回值方法的名称作为初始化方法和销毁方法。
21<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.ExampleBean" init-method="init" destroy-method="cleanup"/>2
111public class ExampleBean {2
3 public void init() {4 // do some initialization work5 }6
7 public void cleanup() {8 // do some destruction work (like releasing pooled connections)9 }10}11
为了简化配置,你可以使用<beans>标签的default-init-method/default-destroy-method属性来为所有子标签中的bean指定默认初始化和销毁方法。但必须注意,Spring 容器保证在为 bean 提供所有依赖项后立即调用配置的初始化回调,因此,在原始 bean 引用上调用了初始化回调,这意味着 AOP 拦截器等尚未应用于 bean。
提示:使用Java代码配置元数据时,使用@Bean的
initMethod和destroyMethod属性来指定初始化和销毁方法。
Bean启动和停止事件回调
可以通过实现Lifecycle接口来定义 Bean 的启动和停止事件回调,当容器本身接收到启动和停止 signal 时(例如,对于运行时的停止/重新启动场景),它将把这些调用级联到在该上下文中定义的所有Lifecycle实现。
251// 实现了Lifecycle接口的Bean2public class MyLifeCycleBean1 implements Lifecycle {4 private boolean status = true;5
6 // 容器start的时候,如果 isRunning==false,则执行该方法7 8 public void start() {9 System.out.println("start");10 }11 12 // 判断Bean是否正在运行13 14 public boolean isRunning() {15 System.out.println("isRunning");16 status = !status;17 return status;18 }19 20 // 容器stop的时候,如果 isRunning==true,则执行该方法21 22 public void stop() {23 System.out.println("stop");24 }25}141public class SpringTest {2 public static void main(String[] args) {3 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyLifeCycleBean1.class);4 ctx.registerShutdownHook();5 ctx.start();6 //ctx.stop(); // 注册关闭钩子后会在容器关闭时调用该方法7 }8}9/*10isRunning11start12isRunning13stop14 */如果想对 start 和 stop 生命周期进行更精细的控制,可以实现SmartLifecycle接口。如通过isAutoStartup方法返回 true 可以实现容器创建后自动启动;通过getPhase()方法返回合适的相位值来控制启动和停止的顺序,该值越大,则越晚执行,越早销毁,默认值为Integer.MAX_VALUE(如果实现的是LifeCycle接口,则默认为0),详细用法请参考Spring官方文档。
不同生命周期机制的执行顺序
如果为一个 bean 配置了多个生命周期机制,当方法名称相同时,该方法将只执行一次。如果方法名称不一致,那么将按照注解配置优先,接口配置次之,XML配置最后执行的原则调用生命周期方法。
1)用 @PostConstruct 注解的方法
2)InitializingBean 回调接口定义的 afterPropertiesSet()方法
3)自定义配置的 init() 方法
4)用 @PreDestroy 注解的方法
5)DisposableBean 回调接口定义的 destroy()方法
6)自定义配置的 destroy() 方法
3. Bean的作用范围
Bean的作用范围决定了Bean的作用域以及在获取对象时是否创建新的实例等,通过scope属性进行配置。
singleton
默认配置的作用范围为singleton,表示单例范围,只创建一次,一般在容器启动时创建,容器销毁时随之销毁。
11<bean id="accountDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl" scope="singleton"/>
prototype
prototype表示原型范围(多例),在每次从容器获取对象时,始终会创建新的实例返回。
11<bean id="accountDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl" scope="prototype"/>与其它作用范围不同的是,Spring不管理原型Bean的完整生命周期,不会调用已配置的生命周期销毁回调。
注意:关于单例bean中注入原型bean的一些细节
在单例Bean中依赖原型Bean时,由于单例Bean只会被IoC容器初始化一次,其依赖也只会被处理一次,因此其依赖的原型Bean也将“隐式”的成为单例。
如何解决这个问题,有两种办法,一种是在使用原型Bean时每次都依赖查找,这样IoC容器会每次都重新创建原型Bean;
另一种办法就是使用@Lookup注解来解决,这种是官方给出解决方案,需注意的是使用@Lookup注解的方法必须声明为抽象方法。
适用于web的作用范围
在Web应用中,提供了一些特殊的bean作用范围,如request、session、application、websocket等,分别与HTTP中的Request、Session、ServletContext、WebSocket作用域一致,这里不做详细讲解,具体可参考Spring的官方文档。
自定义作用范围
Bean 作用域机制是可扩展的,您可以定义自己的范围,甚至重新定义一些内置范围(singleton和prototype除外)。要将自定义范围集成到 Spring 容器中,您需要实现Scope接口。Scope接口有四种方法可以从范围中获取对象,从范围中删除对象,然后销毁它们。
111// 从基础范围返回对象,如果找不到该对象,则创建新实例返回2Object get(String name, ObjectFactory objectFactory)3
4// 从基础范围中删除该对象并返回删除的值,如果找不到该对象则返回null5Object remove(String name)6 7// 注册在销毁作用域或销毁作用域中的指定对象时作用域应执行的回调8void registerDestructionCallback(String name, Runnable destructionCallback)9 10// 获取基础范围的会话标识符,每个范围的标识符都不相同。对于会话范围的实现,此标识符可以是会话标识符。11String getConversationId()在编写自定义Scope实现之后,您需要使 Spring 容器意识到您的新作用域。通过以下方法在 Spring 容器中注册新的Scope。
21Scope threadScope = new SimpleThreadScope();2beanFactory.registerScope("thread", threadScope);除了使用程序进行Scope的注册外,您还可以通过使用CustomScopeConfigurer类以声明方式进行Scope注册,如以下示例所示:
151......2
3 <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomScopeConfigurer">4 <property name="scopes">5 <map>6 <entry key="thread">7 <bean class="org.springframework.context.support.SimpleThreadScope"/>8 </entry>9 </map>10 </property>11 </bean>12
13 <bean id="thing2" class="x.y.Thing2" scope="thread"/>14
15......从 Spring 3.0 开始,线程作用域可用,但默认情况下未注册。有关更多信息,请参见SimpleThreadScope的文档。
4. Bean的感知接口
感知接口(Aware)表示 Bean 向容器声明它们需要某种基础结构依赖性。这些接口回调在填充常规 bean 属性之后,但在初始化回调(例如InitializingBean,afterPropertiesSet或自定义 init-method)之前调用。
ApplicationContextAware
当 ApplicationContext 在创建实现ApplicationContextAware接口的对象实例时,该实例将获得对该ApplicationContext的引用。
41// ApplicationContextAware接口定义2public interface ApplicationContextAware {3 void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;4}
BeanNameAware
当 ApplicationContext 在创建实现BeanNameAware接口的类时,该类将获得对在其关联的对象定义中定义的名称的引用。
41// BeanNameAware接口定义2public interface BeanNameAware {3 void setBeanName(String name) throws BeansException;4}
其它感知接口
| Name | Injected Dependency |
|---|---|
| ApplicationEventPublisherAware | ApplicationContext的事件发布者 |
| BeanFactoryAware | BeanFactory |
| BeanClassLoaderAware | 类加载器(用于加载 Bean 类) |
| LoadTimeWeaverAware | 编织器(用于在加载时处理类定义) |
| MessageSourceAware | 解析消息的配置策略(支持参数化和国际化) |
| NotificationPublisherAware | Spring JMX 通知发布者 |
| ResourceLoaderAware | 资源加载器(用于低级资源访问) |
| ServletConfigAware | 当前容器运行的ServletConfig(仅在Web环境有效) |
| ServletContextAware | 当前容器运行的ServletContext(仅在Web环境有效) |
注意:使用这些接口会将您的代码与 Spring API 绑定在一起,并且不遵循“控制反转”样式。因此,我们建议将它们用于需要以编程方式访问容器的基础结构 Bean。
5. Bean的自动装配
Spring 容器可以自动装配协作 Bean 之间的关系,即在创建对象后,自动从容器中查找所需的依赖并进行注入。这可以大大减少指定属性或构造函数参数的需要,并且当类中新增依赖项时,无需修改配置即可自动满足该依赖项。
自动装配的模式共有四种,通过bean标签的autowire属性来指定。
| Mode | Explanation |
|---|---|
| no(默认) | 不进行自动装配, 仅由 ref 属性来定义 Bean 之间的依赖关系,可以提供更好的控制和清晰度。 |
| byName | 按属性名称自动装配,Spring通过属性名在容器中查找匹配的依赖 Bean 进行注入。 |
| byType | 按属性类型自动装配,如果查找到唯一匹配的依赖Bean,则进行注入。但如果查找到多个,则引发致命异常。 |
| constructor | 类似于byType,适用于构造函数参数的自动装配。不同的是,如果未查找到匹配的依赖Bean也会引发致命异常。 |
151<!-- byName 自动注入 -->2<bean id="myStudent" class="com.bjpowernode.ba04.Student" autowire="byName">3 <property name="name" value="李四"/>4 <property name="age" value="22" />5 <!--引用类型的赋值-->6 <!--<property name="school" ref="mySchool" />-->7</bean>8
9<!-- byType 自动注入 -->10<bean id="myStudent" class="com.bjpowernode.ba05.Student" autowire="byType">11 <property name="name" value="张三"/>12 <property name="age" value="26" />13 <!--引用类型的赋值-->14 <!--<property name="school" ref="mySchool" />-->15</bean>如果使用ByType自动装配匹配到了多个Bean,则可以设置某些Bean的 autowire-candidate属性为false,从候选列表去除。或者也可以通过设置某个Bean的primary属性为true,将其作为主要候选对象。上面两种配置仅对按类型自动装配(byType/Constructor)有效,按名称自动装配(byName)不受其影响。
6. Bean定义继承
在Bean的配置中,可以通过parent属性来指定另一个Bean作为该Bean的 ParentBean, 从而继承一些可复用的配置数据,并可以覆盖某些值或根据需要添加其他值,这是一种模板方法模式的一种体现。
121<!-- ParentBean的定义。一般将 ParentBean 标记为 abstract,用作纯模板 Bean 使用,同时可以省略 class 属性 -->2<bean id="inheritedTestBean" abstract="true" >3 <property name="name" value="parent"/>4 <property name="age" value="1"/>5</bean>6
7<!-- ChildBean的定义-->8<bean id="inheritsWithDifferentClass" class="org.springframework.beans.DerivedTestBean" init-method="initialize"9 parent="inheritedTestBean"> 10 <property name="name" value="override"/>11 <!-- 将从 ParentBean 继承 age 属性的注入 -->12</bean>ChildBean 可以从 ParentBean 继承Bean的作用范围、生命周期、属性注入等信息,但依赖项、自动装配模式等一些信息始终从子类获取,这需要我们在开发过程中多加关注。
注意:
Spring的继承是对象层面的继承,子类继承父类对象的属性值。因此,Spring 中,不同类之间可以互相继承。
Java是类层面的继承,继承的是父类的类结构信息。如果用 Java 代码的方式来配置元数据,那么可以直接使用 java 的继承机制来复用元数据的配置信息。
7. Bean其它属性
别名(name/alias)
Bean除了具有唯一性的 id 属性外,还可以定义若干个别名,以兼容不同的业务系统,通常使用name属性或<alias>标签来实现。
61<!-- 配置service,并指定别名,别名以逗号、分号或空格间隔-->2<bean id="accountService" name="accountService2,accountService3" class="org.example.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"/>3
4<!--使用alias标签定义别名-->5<alias name="accountService2" alias="accountServiceA"/>6
初始化顺序(depends-on)
depends-on属性可以指定初始化时间依赖性,也可以在Bean是单例的的情况下指定相应的销毁时间依赖性。
91<bean id="manager" class="ManagerBean" />2<bean id="accountDao" class="x.y.jdbc.JdbcAccountDao" />3
4<!--5 depends-on:在初始化beanOne之前强制先初始化manager和accountDao,在销毁时先销毁manager和accountDao,再销毁beanOne。6-->7<bean id="beanOne" class="ExampleBean" depends-on="manager,accountDao">8 <property name="manager" ref="manager" />9</bean>
懒加载(lazy-init)
单例Bean默认在容器创建时进行实例化,如果想让Bean在使用时再创建,则可指定lazy-init属性为true。
21<!-- 配置 ExpensiveToCreateBean 延迟加载 -->2<bean id="lazy" class="com.something.ExpensiveToCreateBean" lazy-init="true"/>如果需要对多个Bean进行配置,也可以选择beans标签的default-lazy-init属性,为其内部的所有Bean设置可覆盖的默认值。
31<beans default-lazy-init="true">2 <!-- no beans will be pre-instantiated... -->3</beans>提示:如果你使用注解配置,可以使用
@Lazy注解来实现懒加载,并且该注解可以放置在标有@Autowired或@Inject的注入点上。在这种情况下,它导致注入了惰性解析代理。
第四节 依赖注入配置
依赖注入 (Dependency Inject)是控制反转思想的一种实现方式,指的是程序运行过程中,若需要调用另一个对象协助时,无须在代码中创建被调用者,而是依赖于外部容器,由外部容器创建后传递给程序。
1. 构造函数注入
基于构造函数的注入是通过容器调用有参构造函数来完成的,每个参数代表了一个依赖项。
111<!--构造注入,使用name属性2 1. name:指定构造函数参数名称。(在进行set注入时可以使用复合属性名,如student.birthday.year)3 2. value:用于注入基本属性值和String4 3. ref:用于注入引用类型5 4. 集合、空值、内联Bean的注入应使用子标签来完成6-->7<bean id="myStudent" class="com.bjpowernode.ba03.Student">8 <constructor-arg name="myage" value="22" />9 <constructor-arg name="myname" value="李四"/>10 <constructor-arg name="mySchool" ref="mySchool"/>11</bean>对于极少数情况下无法使用构造函数自变量名称的情况(通常,如果字节码是在没有调试信息的情况下编译的),可以通过参数索引进行构造函数的匹配,并且允许在能够推断的情况下省略索引属性。
131<!--构造注入,使用index,参数的位置,构造方法参数从左往右位置是0,1,2-->2<bean id="myStudent2" class="com.bjpowernode.ba03.Student">3 <constructor-arg index="1" value="28"/>4 <constructor-arg index="0" value="张三"/>5 <constructor-arg index="2" ref="mySchool" />6</bean>7
8<!--构造注入,省略index属性-->9<bean id="myStudent3" class="com.bjpowernode.ba03.Student">10 <constructor-arg value="张峰"/>11 <constructor-arg value="28"/>12 <constructor-arg ref="mySchool" />13</bean>还可以使用更为简洁的语法来进行构造函数的注入配置,但这最好是在创建 bean 定义时使用支持自动属性完成的 IDE,否则错字是在运行时而不是设计时发现的。
181<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"2 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"3 xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">6
7 <bean id="thingOne" class="x.y.ThingTwo"/>8 <bean id="thingTwo" class="x.y.ThingThree"/>9
10 <!-- 使用c名称空间简化构造注入的书写方式 11 1. 基本类型使用 c:属性名="属性值"12 2. 引用类型使用 c:属性名_ref="属性值"13 -->14 <bean id="thingOne" class="x.y.ThingOne" 15 c:thingTwo-ref="thingTwo" 16 c:thingThree-ref="thingThree" 17 c:email="[emailprotected]"/>18</beans>提示:使用工厂创建Bean对象时,可以通过
constructor-arg标签进行工厂方法的参数注入,使用方式同构造函数注入一致。
2. Set方法注入
基于Set方法的注入是在对象创建完成后,调用对象的set方法来进行属性注入。
81<bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean> 2
3<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">4 <property name="name" value="test"></property>5 <property name="age" value="21"></property>6 <property name="birthday" ref="now"></property>7</bean>8
类似的,可以使用p名称空间来进行简化书写。
131<beans xmlns="http://www.Springframework.org/schema/beans"2 xmlns:p="http://www.Springframework.org/schema/p"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.Springframework.org/schema/beans 4 http://www.Springframework.org/schema/beans/Spring-beans.xsd">5
6 <bean id="now" class="java.util.Date"></bean> 7 8 <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl4" 9 p:name="test" 10 p:age="21" 11 p:birthday-ref="now"/>12</beans> 13
3. 注入集合属性
顾名思义,就是给类中的集合成员进行属性注入,用的也是set方法注入的方式,只不过变量的数据类型都是集合。
471<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">2 <!-- 给数组注入数据 -->3 <property name="myStrs">4 <set>5 <value>AAA</value>6 <value>BBB</value>7 <value>CCC</value>8 </set>9 </property>10
11 <!-- 注入list 集合数据 -->12 <property name="myList">13 <array>14 <value>AAA</value>15 <value>BBB</value>16 <value>CCC</value>17 </array>18 </property>19
20 <!-- 注入set 集合数据 -->21 <property name="mySet">22 <list>23 <value>AAA</value>24 <value>BBB</value>25 <value>CCC</value>26 </list>27 </property>28
29 <!-- 注入Map 数据 -->30 <property name="myMap">31 <props>32 <prop key="testA">aaa</prop>33 <prop key="testB">bbb</prop>34 </props>35 </property>36
37 <!-- 注入properties 数据 -->38 <property name="myProps">39 <map>40 <entry key="testA" value="aaa"></entry>41 <entry key="testB">42 <value>bbb</value>43 </entry>44 </map>45 </property>46</bean> 47
提示:集合数据分两种,单列集合(array,list,set)和双列集合(map,entry,props,prop),同类型集合注入方式可以兼容。
如果Bean存在继承关系,则可以通过merge属性来合并父类的集合。
231<!-- 定义一个ParentBean,并给adminEmails集合进行注入 -->2<beans>3 <bean id="parent" abstract="true" class="example.ComplexObject">4 <property name="adminEmails">5 <props>6 <prop key="administrator">[emailprotected]</prop>7 <prop key="support">[emailprotected]</prop>8 </props>9 </property>10 </bean>11
12<!-- 定义一个ChildBean,同样给adminEmails集合进行注入 13 1. merge:继承父类集合中的属性,并进行选择性覆盖14-->15 <bean id="child" parent="parent">16 <property name="adminEmails">17 <props merge="true">18 <prop key="sales">[emailprotected]</prop>19 <prop key="support">[emailprotected]</prop>20 </props>21 </property>22 </bean>23<beans>
4. 注入原型Bean
如果某个Bean是单例的,并且依赖了原型Bean,则该原型Bean不能使用上述方式直接注入,必须在每次使用时都创建新的实例。
实现感知接口方式
通过实现感知接口ApplicationContextAware或BeanFactoryAware获取容器的引用,进而调用getBean方法创建原型Bean。
201public class SingleBeanDemo implements BeanFactoryAware {2 private BeanFactory beanFactory;3
4 // 实现感知接口的抽象方法,在创建Bean的时候回调,注入容器的引用5 6 public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {7 this.beanFactory = beanFactory;8 }9 10 // 从容器获取原型Bean实例11 protected PrototypeBeanDemo getPrototypeBeanDemo(){12 this.beanFactory.getBean("prototypeBeanDemo", PrototypeBeanDemo.class)();13 }14 15 // 在业务方法中使用原型Bean16 public void bizMethod() {17 PrototypeBeanDemo prototypeBeanDemo = getPrototypeBeanDemo();18 }19}20
使用Lookup方式
上述方式依赖了Spring框架,并且由程序代码主动获取对象,不符合控制反转的原则,下面将使用XML配置方式由Spring来完成上述代码。
81// SingleBeanDemo 创建为抽象类,并设置 getPrototypeBeanDemo() 方法为抽象方法,待Spring为我们实现2public abstract class SingleBeanDemo {3 protected abstract PrototypeBeanDemo getPrototypeBeanDemo();4 5 public void bizMethod() {6 PrototypeBeanDemo prototypeBeanDemo = getPrototypeBeanDemo();7 }8}101<!-- PrototypeBeanDemo 定义-->2<bean id="prototypeBeanDemo" class="fiona.apple.PrototypeBeanDemo" scope="prototype">3</bean>4
5<!-- SingleBeanDemo 定义6 lookup-method:指定查找方法和查找的原型Bean7-->8<bean id="singleBeanDemo" class="fiona.apple.SingleBeanDemo">9 <lookup-method name="getPrototypeBeanDemo" bean="prototypeBeanDemo"/>10</bean>也可以使用注解方式来配置,并且@Lookup的 value 属性可以根据查找方法声明的返回类型来解析。
91public abstract class SingleBeanDemo {3 /*("prototypeBeanDemo")*/4 protected abstract PrototypeBeanDemo getPrototypeBeanDemo();5
6 public void bizMethod() {7 PrototypeBeanDemo prototypeBeanDemo = getPrototypeBeanDemo();8 }9}注意:
查找方法的签名必须是
<public|protected> [abstract] <return-type> theMethodName(no-arguments)形式。查找方法允许是非 abstract 的,Spring会将原来的方法覆盖。
由于Spring是通过CGLib来实现该方式的,因此该类和查找方法都不能被final修饰。
查找方法不适用于工厂方法和配置类中的@Bean方法,因此在这种情况下,实例并不是由Spring创建的,无法进行动态代理。
注入ObjectFactory
101// 先注入单例的ObjectFactory,再通过getObject方法获取原型Bean的实例2public class SingleBeanDemo {4 5 ObjectFactory<PrototypeBeanDemo> prototypeBeanDemoFactory;6
7 public void bizMethod() {8 PrototypeBeanDemo prototypeBeanDemo = (PrototypeBeanDemo)factory.getObject();9 }10}
5. 循环依赖问题
在进行依赖注入时,如果A依赖B,B依赖C,而C又依赖A,则有可能出现循环依赖问题,抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常,下面将使用案例对三种不同的注入场景进行分析。
51// 有三个需要创建的对象,它们之间相互依赖(A依赖B,B依赖C,而C又依赖A)。2public class StudentA { private StudentB studentB; public void setStudentB(StudentB studentB) { this.studentB = studentB; } public StudentA() { } public StudentA(StudentB studentB) { this.studentB = studentB; } } 3public class StudentB { private StudentC studentC ; public void setStudentC(StudentC studentC) { this.studentC = studentC; } public StudentB() { } public StudentB(StudentC studentC) { this.studentC = studentC; } } 4public class StudentC { private StudentA studentA; public void setStudentA(StudentA studentA) { this.studentA = studentA; } public StudentC() { } public StudentC(StudentA studentA) { this.studentA = studentA; } } 5
通过构造函数注入
首先通过构造函数注入,来描述上面所述的依赖关系,在创建容器时抛出了预期的BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常。
111<bean id="a" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentA"> 2 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="b"></constructor-arg> 3</bean> 4
5<bean id="b" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentB"> 6 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="c"></constructor-arg> 7</bean> 8
9<bean id="c" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentC"> 10 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="a"></constructor-arg> 11</bean> Spring容器会将每一个正在创建的Bean标识符放在一个“当前创建Bean池”中,Bean标识符在创建过程中将一直保持在这个池中。因此如果在创建Bean过程中发现自己已经在“当前创建Bean池”里时将抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常表示循环依赖;而对于创建完毕的Bean将从“当前创建Bean池”中清除掉。
根据上述源码实现分析:Spring容器先创建单例StudentA,StudentA依赖StudentB,然后将A放在“当前创建Bean池”中,此时创建StudentB, StudentB依赖StudentC ,然后将B放在“当前创建Bean池”中,此时创建StudentC,StudentC又依赖StudentA, 但是,此时StudentA已经在池中,所以会报错,因为在池中的Bean都是未初始化完的,所以会依赖错误 ,(初始化完的Bean会从池中移除)。
通过Set方法注入(单例范围)
再来看下使用Set方法注入,并设置Bean范围为单例范围,发现在创建容器时并未抛出异常。
121<bean id="a" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentA" scope="singleton"> 2 <property name="studentB" ref="b"></property> 3</bean> 4
5<bean id="b" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentB" scope="singleton"> 6 <property name="studentC" ref="c"></property> 7</bean> 8
9<bean id="c" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentC" scope="singleton"> 10 <property name="studentA" ref="a"></property> 11</bean> 12
为什么使用Set方法不抛异常呢?关键在于Spring先将Bean对象实例化之后再设置对象属性的。Spring先用构造函数实例化Bean对象 ,然后存入到一个Map中,当StudentA、StudentB、StudentC都实例化完成后,然后才去设置对象的属性,此时StudentA依赖StudentB,就会去Map中取出存在里面的单例StudentB对象,以此类推,不会出来循环的问题喽。
通过Set方法注入(原型范围)
如果Bean的范围为原型,即使使用Set注入,也会抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreationException异常。
121<bean id="a" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentA" scope="prototype"> 2 <property name="studentB" ref="b"></property> 3</bean> 4
5<bean id="b" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentB" scope="prototype"> 6 <property name="studentC" ref="c"></property> 7</bean> 8
9<bean id="c" class="cn.mayday.springrecycledp.demo1.StudentC" scope="prototype"> 10 <property name="studentA" ref="a"></property> 11</bean> 12
因为“prototype”作用域的Bean,Spring容器不进行三级缓存,因此无法提前暴露一个创建中的Bean。
6. 静态变量注入
我们封装工具类的时候,大多数提供的是静态方法,而静态方法只能访问静态变量,此时,则需要将我们所需的依赖注入到静态变量中。
通过Set方法注入
91public class RedisLockUtil {3 private static RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;4 5 6 public void setRedisTemplate(RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate) {7 RedisLockUtil.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;8 }9 }
使用@PostConstruct注解
121public class RedisLockUtil {3 private static RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;4 5 6 private RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate_copy;7
8 9 public void init(){10 RedisLockUtil.redisTemplate=redisTemplate_copy;11 }12 }
7. 普通类使用Bean
如果某个类是一个普通的Java,并且并没有被Spring容器所管理,那么如何使用Spring容器创建的Bean实例呢?
SpringUtils工具类
定义一个工具类,实现容器的感知接口,通过静态方法向外部提供获取Bean的功能。
371public class SpringUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {3 private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;4
5 6 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {7 SpringUtils.applicationContext = applicationContext;8 }9
10 public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) {11 return applicationContext.getBean(requiredType);12 }13
14 public static <T> T getBean(String beanName) {15 return (T) applicationContext.getBean(beanName);16 }17
18 public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) {19 return applicationContext.getBean(requiredType, args);20 }21
22 public static <T> T getBean(String beanName, Object... args) {23 return (T) applicationContext.getBean(beanName, args);24 }25
26 public static <T> T getBean(String beanName, Class<T> requiredType) {27 return (T) applicationContext.getBean(beanName, requiredType);28 }29
30 public int getBeanDefinitionCount(){31 return applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionCount();32 }33
34 public String[] getBeanDefinitionNames(){35 return applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();36 }37}
静态化Bean
修改 Bean 的代码,在初始化回调时将 Bean 的 this 指针设置到一个静态变量中。
161public class FundDispatchLogUtils {3 // 定义一个静态变量,用于保存this指针4 private static FundDispatchLogUtils instance;5
6 // 把this保存在静态变量中7 8 public void init() {9 instance = this;10 }11
12 // 提供获取this的静态方法13 public static FundDispatchLogUtils getInstance() {14 return instance;15 }16}
8. 自定义类型处理器
Spring通过类型转换器把配置文件中字符串类型的数据,转换成了对象中成员变量对应类型的数据,进而完成了注入,当Spring内部没有提供特定类型的转换器时,那么就需要程序员自己定义类型转换器。
实现 Converter 接口
221/**2* 自定义类型转换器,完成String->Date的转换。3*/4public class MyDateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {5 private String pattern;6
7 public void setPattern(String pattern) {8 this.pattern = pattern;9 }10 11 12 public Date convert(String source) {13 Date date = null;14 try {15 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);16 date = sdf.parse(source);17 } catch (ParseException e) {18 e.printStackTrace();19 }20 return date;21 }22}
注册自定义类型转换器
121<!-- 创建 MyDateConverter 的对象-->2<bean id="myDateConverter" class="com.baizhiedu.converter.MyDateConverter">3 <property name="pattern" value="yyyy-MM-dd"/>4</bean>5
6<!-- 注册类型转换器7 1. 目的:告知Spring框架,我们所创建的MyDateConverter是一个类型转换器8 2. 注意:ConversionSeviceFactoryBean 定义 id属性 值必须是 conversionService9-->10<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">11 <property name="converters" ref="myDateConverter"></property>12</bean>
第五节 基于注解的IOC配置
Spring从2.x版本开始,提供了注解方式来配置IOC容器和注册Bean, 充分利用程序中提供的上下文,使得配置更加简短和整洁。
在使用基于XML配置的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来构建IOC容器时,需要在XML中开启注解配置开关。
131 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">9
10 <!-- 开启注解配置开关 -->11 <context:annotation-config/>12
13</beans>开启注解配置开关会自动注册下面一些后处理器,并且在定义它的应用程序上下文中扫描Bean上的注解。
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
也可以使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext直接基于注解配置来构建容器,然后使用@ImportResuorce注解导入XML配置。
51("classpath:beans.xml")3public class AppConfig {4
5}注意
注解配置对源代码存在侵入,并且配置分散不利于维护,在使用时需结合实际情况选用。
Spring优先对注解配置的属性进行注入,如果在XML中配置了相同的属性,那么将会对之前的配置进行覆盖。
1. 使用@Component标记组件
@Component 注解作用于类、接口、枚举或其它注解之上,标记该元素为Spring的一个组件,唯一的 value 属性用于指定组件的名称。
41// 定义一个Bean,id为类名的首字母小写(userServiceImpl)2("userServiceImpl")3public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {4}为了区分该组件属于持久层、服务层或是控制层,分别为此定义了三个语义性注解:@Repository、@Service、@Controller。这在将来可能还会有一些特殊的语义,如@Repository被支持作为持久层中自动异常转换的标记等。
2. 使用@ComponnetScan进行组件扫描
@ComponentScan 一般作用于 @Configuration 类上,用于自动检测标记的组件,并将构造型类向ApplicationContext注册相应的BeanDefinition实例。
61(basePackages = "org.example") // basePackages:扫描的包名,以分号、逗号或空格分隔。3// @ComponentScan("org.example")4public class AppConfig {5 ...6}等效的XML配置如下。
21<!-- 配置组件扫描,并隐式开启注解配置功能(<context:annotation-config>) -->2<context:component-scan base-package="org.example"/>
配置扫描过滤器
默认情况下,会扫描所有被 @Component 及其衍生注解标记的组件,你可以通过includeFilters和excludeFilters属性设置过滤器来修改和扩展此行为,过滤器的类型和描述如下列表所示。
| Filter Type | Example Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| annotation (default) | org.example.SomeAnnotation | 在目标组件的类型级别上存在的注解。 |
| assignable | org.example.SomeClass | 目标组件可分配给(扩展或实现)的类(或接口)。 |
| aspectj | org.example..*Service+ | 目标组件要匹配的 AspectJ 类型表达式。 |
| regex | org.example.Default.* | 要与目标组件类名称匹配的正则表达式。 |
| custom | org.example.MyTypeFilter | org.springframework.core.type .TypeFilter 接口的自定义实现。 |
141/**2 @Configuration:声明该类为一个配置类3 @ComponentScan:组件扫描4 basePackages:扫描的包名5 includeFilters:包含过滤器,仅扫描满足条件的组件6 excludeFilters:排除过滤器,不扫描满足条件的组件7*/8(basePackages = "org.example",10 includeFilters = (type = FilterType.REGEX, pattern = ".*Stub.*Repository"),11 excludeFilters = (Repository.class))12public class AppConfig {13 ...14}等效的XML配置如下。
61<beans>2 <context:component-scan base-package="org.example">3 <context:include-filter type="regex" expression=".*Stub.*Repository"/>4 <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>5 </context:component-scan>6</beans>也可以参考如下,下面是一个线上项目中使用的案例。
111(exclude = { DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class })2(basePackages = { "com.szkingdom.kfms.**", "com.szkingdom.fs.**", "com.szkingdom.koca.**" })5(basePackages = { "com.szkingdom.**.dao.**" })6public class KfmsBootApplication {7 public static void main(String[] args) {8 SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(KfmsBootApplication.class);9 springApplication.run(args);10 }11}提示: 你可以将 useDefaultFilters (或 use-default-filters)属性设置为 false 来禁止移除默认过滤器,这将禁用对带有
@Component,@Repository,@Service,@Controller或@Configuration注解的类的自动检测。
自定义名称生成策略
在扫描过程中自动检测到某个组件时,其 bean 名称由该扫描器已知的BeanNameGenerator策略生成。默认使用配置的 value 属性值,如果未配置则使用类名的首字母小写作为 bean 名称。
111// 使用 value 属性值 myMovieLister 作为 bean 名称2("myMovieLister")3public class SimpleMovieLister {4 // ...5}6
7// 使用 movieFinderImpl 作为 bean 名称8public class MovieFinderImpl implements MovieFinder {10 // ...11}如果你想对名称生成策略进行修改,可以实现 BeanNameGenerator 接口,提供无参构造函数,然后在 @ComponentScan 注解的 nameGenerator 属性进行配置。
61// nameGenerator:指定自定义名称生成策略2(basePackages = "org.example", nameGenerator = MyNameGenerator.class)4public class AppConfig {5 ...6}等效的XML配置如下:
41<beans>2 <context:component-scan base-package="org.example"3 name-generator="org.example.MyNameGenerator" />4</beans>
生成组件索引
在大型应用程序中启动时,组件扫描可能会花费不短的时间,可以通过在编译时创建候选静态列表(索引)来提高大型应用程序的启动性能。
91<!-- 在每个包含组件的模块中加入该依赖,则在编译时会自动生成索引到 META-INF/spring.components 文件中 -->2<dependencies>3 <dependency>4 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>5 <artifactId>spring-context-indexer</artifactId>6 <version>5.1.3.RELEASE</version>7 <optional>true</optional>8 </dependency>9</dependencies>注意
如果ApplicationContext在启动时检测到组件索引,则会直接使用索引,而不会再进行组件扫描。这意味着你必须给所有存在组件的模块都加上依赖。
可以使用全局属性
spring.index.ignore=true来忽略组件索引,回退为组件扫描的方式。
3. 配置Bean的属性
使用@Scope配置组件的作用范围
组件默认注册为 singleton 范围,如果相对其进行修改,可以使用 @Scope 注解。
51("prototype")2public class MovieFinderImpl implements MovieFinder {4 // ...5}注意:
与XML中的scope属性不同,@Scope属性仅在具体的 bean 类(对于带注解的组件)或工厂方法(对于@Bean方法)上有效,不能被继承。
可以实现 ScopeMetadataResolver 接口提供用于范围解析的自定义策略,而不是依赖于基于注解的方法。
51(basePackages = "org.example", scopeResolver = MyScopeResolver.class)3public class AppConfig {4 ...5}等效XML配置
31<beans>2 <context:component-scan base-package="org.example" scope-resolver="org.example.MyScopeResolver"/>3</beans>
使用某些非单作用域时,可能有必要为作用域对象生成代理,可以使用 scoped-proxy 属性配置,下面配置产生标准的JDK动态代理。
61// scopedProxy:选择动态代理,可选 no、interfaces 和 targetClass2(basePackages = "org.example", scopedProxy = ScopedProxyMode.INTERFACES)4public class AppConfig {5 ...6}等效XML配置如下:
31<beans>2 <context:component-scan base-package="org.example" scoped-proxy="interfaces"/>3</beans>
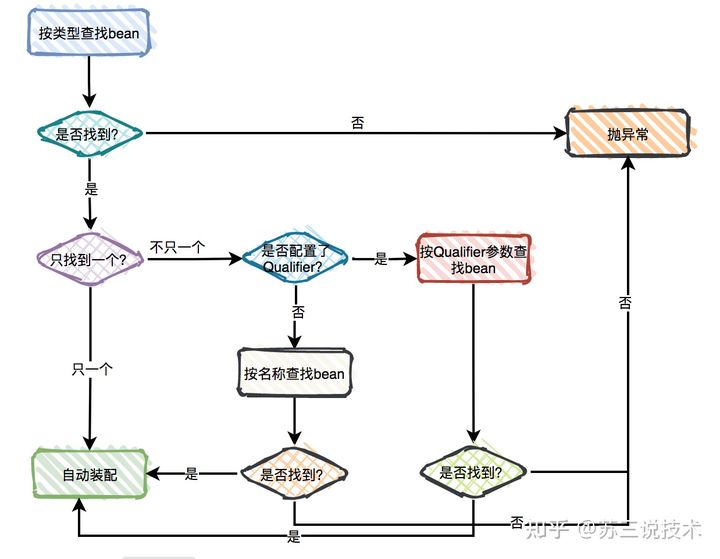
4. 使用@Autowired进行自动注入
@Autowired 注解一般用于引用类型属性的自动注入,可作用于构造器、方法、参数、成员变量和注解上。
应用于单个变量
如果被注解的是单个变量,则进行唯一性匹配,即优先按类型进行匹配,如果存在多个匹配的类型,再使用变量名称进行匹配。
41public class MovieRecommender {2 3 private CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;4}
应用于数组或单列集合
如果被注解的是数组或单列集合,则将该类型的所有 Bean 按照定义顺序依次注入到其中。
71public class MovieRecommender {2 3 private MovieCatalog[] movieCatalogs;4 5 6 private Set<MovieCatalog> movieCatalogs;7}如果你想精确控制它们的注入顺序,可以实现 Ordered接口或使用@Order/@Priority注解。
应用于双列集合
如果被注解的是一个双列集合(Key为String类型),则同样可以注入所有该类型的 Bean,并且使用 Bean 的id属性作为键值对的key值。
41public class MovieRecommender {2 3 private Map<String, MovieCatalog> movieCatalogs;4}
应用于构造函数
如果被注解的是构造函数,则表示使用该函数来实例化 Bean 对象,通过构造参数来进行属性注入。
81public class MovieRecommender {2 private final CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;3
4 5 public MovieRecommender(CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao) {6 this.customerPreferenceDao = customerPreferenceDao;7 }8}你可以注解多个构造函数作为“候选者”,Spring会选择参数最多的那个进行实例化,但必须保证它们的 required 属性都为false。
171public class MovieRecommender {2 private final CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;3 private final MovieFinder movieFinder;4
5 // required 属性必须修改为false6 (required = false)7 public MovieRecommender(CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao) {8 this.customerPreferenceDao = customerPreferenceDao;9 }10 11 // required 属性必须修改为false12 (required = false)13 public MovieRecommender(CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao, MovieFinder movieFinder) {14 this.customerPreferenceDao = customerPreferenceDao;15 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;16 }17}如果未对构造函数使用 @Autowired 注解,则默认使用无参构造进行实例化。如果也没有无参构造,那么必须保证存在唯一的有参构造。
应用于其它方法
@Autowired 也可以支持注解 Bean 中的其它类型方法,但一般来说,传统 setter 方法使用的更多。
91public class SimpleMovieLister {2 private MovieFinder movieFinder;3
4 // 注解 setter 方法 :先对 movieFinder 参数进行注入,然后调用 setMovieFinder 方法5 6 public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {7 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;8 }9}111public class MovieRecommender {2 private MovieCatalog movieCatalog;3 private CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;4
5 // 注解任意方法6 @Autowired7 public void prepare(MovieCatalog movieCatalog, CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao) {8 this.movieCatalog = movieCatalog;9 this.customerPreferenceDao = customerPreferenceDao;10 }11}
依赖必须性
在自动注入时,如果无法找到合适的 Bean,则抛出 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 异常,可以通过 required 属性对此进行修改。
81public class SimpleMovieLister {2 private MovieFinder movieFinder;3
4 (required = false)5 public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {6 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;7 }8}
注入内置 Bean
使用 @Autowired 注解可以直接注入常用的可解决依赖项,而无需进行特殊设置,如BeanFactory、ApplicationContext、Environment、ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher以及MessageSource等。
41public class MovieRecommender {2 3 private ApplicationContext context;4}
使用泛型作为自动装配限定符
除了@Qualifier注解外,您还可以将 Java 泛型类型用作自动装配的匹配条件。
141public class MyConfiguration {3 // 实例化一个 StringStore 对象,StringStore 实现了 Store<String>4 5 public StringStore stringStore() {6 return new StringStore();7 }8
9 // 实例化一个 IntegerStore 对象,IntegerStore 实现了 Store<Integer>10 11 public IntegerStore integerStore() {12 return new IntegerStore();13 }14}41private Store<String> s1; // 注入StringStore3private Store<Integer> s2; // 注入 IntegerStore
5. 使用@Resource进行自动注入
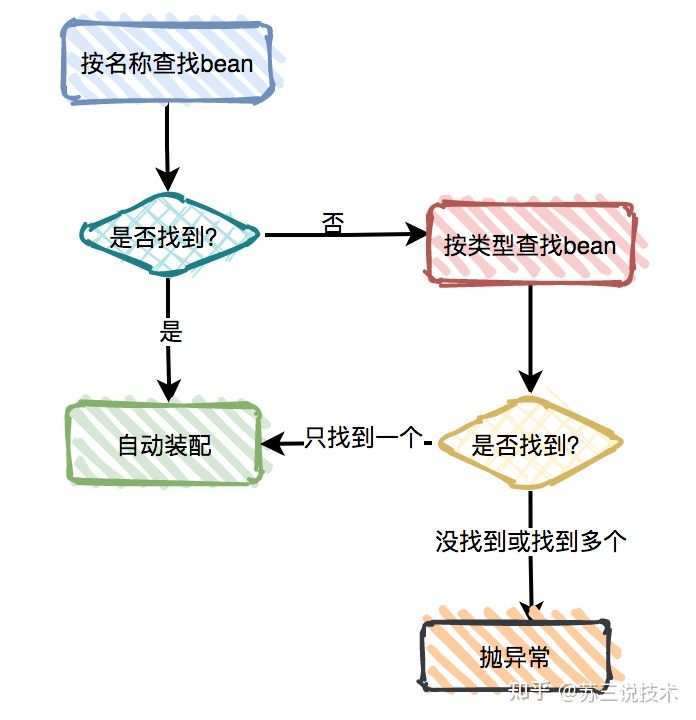
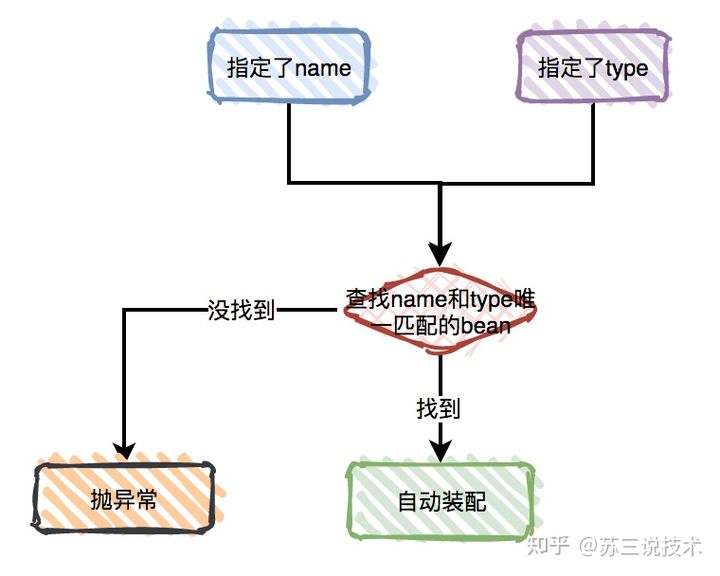
@Resource 是JSR-250定义的注解,与@Autowired都是用于属性注入,可以作用于类、成员变量和方法上。常用的属性有name和type。
未指定name和type
同时指定name和type
仅指定name
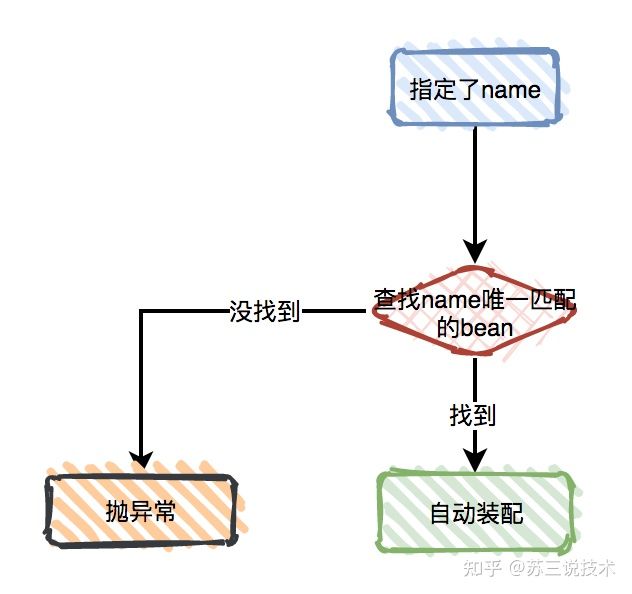
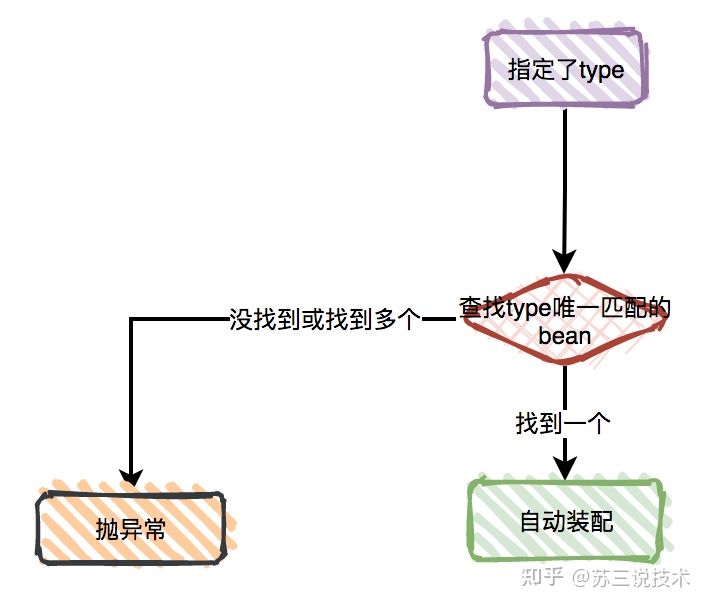
仅指定type
151public class SimpleMovieLister {2 private MovieFinder movieFinder;3
4 // 仅按 myMovieFinder 名称匹配,失败则抛异常5 (name="myMovieFinder")6 public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {7 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;8 }9 10 // 优先按 movieFinder 名称匹配,失败则按类型匹配11 12 public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {13 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;14 }15}注意事项
数据注入注解@Autowired、@Inject、@Resource和@Value由BeanPostProcessor处理。这意味着您不能在自己的BeanPostProcessor或BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型(如果有)中应用这些注解。必须使用 XML 或 Spring @Bean方法显式“连接”这些类型。
6. 用于注入数据的其他注解
使用@Value注入字面量
@Value注解一般用于字面量的注入,并且会解析${}从环境中取值进行替换。
181("classpath:beans.xml")3public class AppConfig {4
5 ("${jdbc.url}")6 private String url;7
8 ("${jdbc.username}")9 private String username;10
11 ("${jdbc.password}")12 private String password;13
14 15 public DataSource dataSource() {16 return new DriverManagerDataSource(url, username, password);17 }18}注意 @Value注解会优先去容器中查找名称一致的Bean进行注入,只有未找到合适的Bean时,才会进行字面量注入。
使用@Required标记属性的必需性
@Required 通常作用于 setter 方法之上,标记某个属性在实例化 Bean 时必须被注入,否则就会抛出 BeanInitializationException 异常,具体请参考 RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 的实现。
91public class Student {2 private String name;3
4 // 标记 name 属性必须被注入(注意:即使注入 NULL 也算被注入了,@Required 不做空指针检测)5 6 public void setName(String name) {7 this.name = name;8 }9}等效的XML配置如下。
41<!-- student bean的定义,必须对 name 属性进行注入 -->2<bean id = "student" class="com.how2java.w3cschool.required.Student">3 <property name = "name" value="派大星"/>4</bean>
使用@Primary调整自动注入优先级
使用自动装配可能存在多个适合注入的候选对象,@Primary 注解可以指定某个 Bean 作为主 Bean,如果候选对象列表中存在唯一的主 Bean,则使用该值进行注入。
91public class MovieConfiguration {3 4 // 指定该Bean为主Bean,优先进行注入5 public MovieCatalog firstMovieCatalog() { ... }6
7 8 public MovieCatalog secondMovieCatalog() { ... }9}等效的XML配置如下。
21<bean id="firstMovieCatalog" class="example.SimpleMovieCatalog" primary="true"/>2<bean id="secondMovieCatalog" class="example.SimpleMovieCatalog"/>
使用@Qualifier进行匹配限定
@Qualifier 用于指定一个限定符,以缩小自动装配的匹配范围,可作用于成员变量、构造方法参数或其它方法参数之上。
131public class MovieRecommender {2 3 ("main") // 成员变量上使用@Qualifier(指定匹配的限定符为main)4 private MovieCatalog movieCatalog;5 6 private CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;7 8 // 方法参数上使用@Qualifier9 10 public void prepare(("main") CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao) {11 this.customerPreferenceDao = customerPreferenceDao;12 }13}假设 MovieCatalog 类型的 Bean 配置如下,则会与 SimpleMovieCatalog1 进行连接。
101("main")3public class MovieCatalog extends SimpleMovieCatalog1{4}5
6("action")8public class MovieCatalog extends SimpleMovieCatalog2{9}10
同等效果的XML配置如下。
71<bean id="simpleMovieCatalog1" class="example.SimpleMovieCatalog1">2 <qualifier value="main"/>3</bean>4
5<bean id="simpleMovieCatalog2" class="example.SimpleMovieCatalog2">6 <qualifier value="action"/> 7</bean>提示:
每个Bean都会将 id 属性作为默认的限定符值,如上例也可以使用@Qualifier("simpleMovieCatalog2")来连接另一个实例。
@Qualifier对集合类型变量也有效,将会在注入前限定匹配的范围(注意:Bean的限定符值并不是唯一的)。
自定义限定符
可以基于@Qualifier自定义一些组合注解,并对属性做一些修改,只有当全部属性都匹配时,才会加入候选列表。
81// 定义组合注解 @MovieQualifier2({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER})3(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)4public @interface MovieQualifier {6 String genre();7 Format format();8}41// 限定自动注入的匹配范围,只有当format=Format.VHS, genre="Action"时才进行匹配2(format=Format.VHS, genre="Action")4private MovieCatalog actionVhsCatalog;111<bean class="example.SimpleMovieCatalog">2 <qualifier type="MovieQualifier">3 <attribute key="format" value="VHS"/>4 <attribute key="genre" value="Comedy"/>5 </qualifier>6</bean>7
8<bean class="example.SimpleMovieCatalog">9 <meta key="format" value="DVD"/>10 <meta key="genre" value="Action"/>11</bean>也可以使用CustomAutowireConfigurer来声明自定义的限定符注解,而不使用组合注解的方式。
71<bean id="customAutowireConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.CustomAutowireConfigurer">2 <property name="customQualifierTypes">3 <set>4 <value>example.CustomQualifier</value>5 </set>6 </property>7</bean>
7. 使用JSR-330注解(了解)
JSR-330注解是Java标准定义的依赖注入注解,Spring从3.0版本开始提供对这些注解的支持。
61<!--引入JSR-330注解的相关依赖-->2<dependency>3 <groupId>javax.inject</groupId>4 <artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>5 <version>1</version>6</dependency>
@ManagedBean/@Named: 组件标记
javax.annotation.ManagedBean或javax.inject.Named可用于组件扫描,作用与@Component类似。
151import javax.inject.Inject;2import javax.inject.Named;3
4("movieListener") // @ManagedBean("movieListener") could be used as well5public class SimpleMovieLister {6
7 private MovieFinder movieFinder;8
9 10 public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {11 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;12 }13
14 // ...15}并且可以使用与Spring注解完全相同的方式来配置组件扫描,如以下示例所示:
51(basePackages = "org.example")3public class AppConfig {4 ...5}
@Inject/@Named: 依赖注入
可以使用javax.inject.Inject进行属性注入,作用与@Autowired类似。
161import javax.inject.Inject;2
3public class SimpleMovieLister {4
5 private MovieFinder movieFinder;6
7 8 public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {9 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;10 }11
12 public void listMovies() {13 this.movieFinder.findMovies(...);14 ...15 }16}如果要为注入的依赖项使用限定名称,还可以使用@Named注解。
141import javax.inject.Inject;2import javax.inject.Named;3
4public class SimpleMovieLister {5
6 private MovieFinder movieFinder;7
8 9 public void setMovieFinder(("main") MovieFinder movieFinder) {10 this.movieFinder = movieFinder;11 }12
13 // ...14}@Inject没有required属性,但可以和java.util.Optional或@Nullable一起使用设置属性是否为必输。
151public class SimpleMovieLister {2
3 4 public void setMovieFinder(Optional<MovieFinder> movieFinder) {5 ...6 }7}8 9public class SimpleMovieLister {10
11 12 public void setMovieFinder( MovieFinder movieFinder) {13 ...14 }15}
JSR-330 标准注解的局限性
当使用标准注解时,您应该知道某些重要功能不可用,如下表所示:
| Spring | javax.inject.* | javax.inject 限制/注解 |
|---|---|---|
| @Autowired | @Inject | @Inject没有“必需”属性。可以与 Java 8 的Optional一起使用。 |
| @Component | @Named/@ManagedBean | JSR-330 不提供可组合的模型,仅提供一种识别命名组件的方法。 |
| @Scope("singleton") | @Singleton | JSR-330 的默认范围类似于 Spring 的prototype。但是,为了使其与 Spring 的常规默认设置保持一致,默认情况下,在 Spring 容器中声明的 JSR-330 bean 为singleton。为了使用singleton以外的范围,您应该使用 Spring 的@Scope注解。 javax.inject还提供@Scope注解。但是,此仅用于创建自己的 注解。 |
| @Qualifier | @ Qualifier/@ Named | javax.inject.Qualifier只是用于构建自定义限定符的元 注解。可以通过javax.inject.Named关联具体的String限定词(如带有值的 Spring 的@Qualifier)。 |
| @Value | - | no equivalent |
| @Required | - | no equivalent |
| @Lazy | - | no equivalent |
| ObjectFactory | Provider | javax.inject.Provider是 Spring 的ObjectFactory的直接替代方法,只是使用较短的get()方法名。它也可以与 Spring 的@Autowired或未注解的构造函数和 setter 方法结合使用。 |
第六节 基于 Java 的IOC配置
基于Java的容器配置指的是在 Java 代码中使用注解来配置 Spring 容器,其中最核心的两个注解为@Configuration和@Bean。其中@Configuration 标记某个类为 Spring 的配置类组件,作为 Bean 定义的来源,而 @Bean 通过标记类中的公共方法进行 Bean 的定义。
1. 使用@Bean定义Bean
默认情况下,bean 名称为方法名称,value 为返回的对象,类型为返回值类型。
81public class AppConfig {3 // 定义一个Bean:transferService -> com.acme.TransferServiceImpl4 5 public TransferServiceImpl transferService() {6 return new TransferServiceImpl();7 }8}等效的 XML 配置如下:
31<beans>2 <bean id="transferService" class="com.acme.TransferServiceImpl"/>3</beans>
2. 配置Bean的属性
修改Bean的名称和描述
可以使用name属性来指定bean的名称,或通过指定多个名称来设置别名。
181public class AppConfig {3
4 // 定义一个Bean指定名称为:myThing5 (name = "myThing")6 public Thing thing() {7 return new Thing();8 }9}10
11public class AppConfig {13 // 定义一个Bean,并指定多个名称14 ({"dataSource", "subsystemA-dataSource", "subsystemB-dataSource"})15 public DataSource dataSource() {16 // instantiate, configure and return DataSource bean...17 }18}在必要的时候,也可以通过@Description提供更详细的文本描述。
101public class AppConfig {3
4 // 定义一个Bean,并添加描述信息5 6 ("Provides a basic example of a bean")7 public Thing thing() {8 return new Thing();9 }10}
设置生命周期回调
@Bean 注解支持指定任意的初始化和销毁回调方法,就像 XML 配置中的init-method和destroy-method属性一样。
291public class BeanOne {2
3 public void init() {4 // initialization logic5 }6}7
8public class BeanTwo {9
10 public void cleanup() {11 // destruction logic12 }13}14
15public class AppConfig {17
18 // 指定初始化方法19 (initMethod = "init")20 public BeanOne beanOne() {21 return new BeanOne();22 }23
24 // 指定销毁方法25 (destroyMethod = "cleanup")26 public BeanTwo beanTwo() {27 return new BeanTwo();28 }29}你也可以在构造期间直接调用 init() 方法同样有效。
101public class AppConfig {3 4 5 public BeanOne beanOne() {6 BeanOne beanOne = new BeanOne();7 beanOne.init();8 return beanOne;9 }10}除上之外,任何使用 @Bean 注解定义的类都支持常规的生命周期回调,并且可以使用 JSR-250 中的@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解。同样的,如果 bean 实现了InitializingBean,DisposableBean或Lifecycle,则容器将调用它们各自的方法。
注意:默认情况下,使用Java 配置时会自动将公共的
close或shutdown方法注册为销毁回调,可以使用下面方式去除。41(destroyMethod="")2public DataSource dataSource() throws NamingException {3return (DataSource) jndiTemplate.lookup("MyDS");4}
修改Bean的范围
使用 Java 配置默认生成的 Bean 范围是 singleton,你可以使用 @Scope 注解来修改它。
91public class MyConfiguration {3
4 5 ("prototype")6 public Encryptor encryptor() {7 // ...8 }9}提示:有关scoped-proxy属性的使用请参考官方文档!
3. Bean的依赖注入
方法参数方式
创建Bean的方法可以具有任意数量的参数,这些参数描述构建该 bean 所需的依赖关系,解析机制与基于构造函数的依赖注入几乎相同。
91public class AppConfig {3
4 // transferService -> com.acme.TransferServiceImpl5 6 public TransferService transferService(AccountRepository accountRepository) {7 return new TransferServiceImpl(accountRepository);8 }9}
方法调用方式
除了使用方法参数来定义依赖外,还可以通过方法调用来定义 Bean 之间的依赖。
151public class AppConfig {3
4 // 定义一个 beanOne,并通过方法调用依赖 beanTwo5 6 public BeanOne beanOne() {7 return new BeanOne(beanTwo());8 }9
10 // 定义一个 beanTwo11 12 public BeanTwo beanTwo() {13 return new BeanTwo();14 }15}等效的 XML 配置如下:
71<beans>2 <bean id="beanOne" class="com.acme.services.BeanOne">3 <constructor-arg name="beanTwo" ref="beanTwo"/>4 </bean>5 6 <bean id="beanTwo" class="com.acme.services.BeanTwo"></bean>7</beans>注意:仅当在
@Configuration类中声明@Bean方法时,此声明 bean 间依赖性的方法才有效。您不能通过使用普通@Component类来声明 Bean 间的依赖关系。
关于方法调用定义 Bean 依赖的进一步说明
请看如下示例,
clientDao()在clientService1()中被调用过一次,在clientService2()中被调用过一次,但是这两次调用返回的却是同一个实例。2712public class AppConfig {3// 定义一个Bean:clientService15public ClientService clientService1() {7ClientServiceImpl clientService = new ClientServiceImpl();8// 第一次调用 clientDao()9clientService.setClientDao(clientDao());10return clientService;11}12// 定义一个Bean:clientService214public ClientService clientService2() {16ClientServiceImpl clientService = new ClientServiceImpl();17// 第二次调用 clientDao()18clientService.setClientDao(clientDao());19return clientService;20}21// 定义一个单例Bean:clientDao23public ClientDao clientDao() {25return new ClientDaoImpl();26}27}因为所有
@Configuration类在启动时都使用CGLIB子类化。在子类中,子方法在调用父方法并创建新实例之前,首先检查容器中是否有任何缓存(作用域)的 bean。
类成员注入
Configuration类也是一个Bean,因此可以使用@Autowired或@Value注入需要的依赖,在方法中使用。
501public class ServiceConfig {3
4 // 注入依赖:accountRepository5 6 private AccountRepository accountRepository;7
8 // 定义一个bean:transferService9 10 public TransferService transferService() {11 // 使用注入的依赖12 return new TransferServiceImpl(accountRepository);13 }14}15
16public class RepositoryConfig {18 private final DataSource dataSource;19
20 // 注入依赖:dataSource21 22 public RepositoryConfig(DataSource dataSource) {23 this.dataSource = dataSource;24 }25
26 // 定义一个Bean:accountRepository27 28 public AccountRepository accountRepository() {29 // 使用注入的依赖30 return new JdbcAccountRepository(dataSource);31 }32}33
34// 总配置类35({ServiceConfig.class, RepositoryConfig.class})37public class SystemTestConfig {38
39 40 public DataSource dataSource() {41 // return new DataSource42 }43}44
45// 测试46public static void main(String[] args) {47 ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SystemTestConfig.class);48 TransferService transferService = ctx.getBean(TransferService.class);49 transferService.transfer(100.00, "A123", "C456");50}但是这种方式是不被推荐的,因为Configuration类在上下文初始化期间非常早地处理的,并且强制以这种方式注入的依赖项(如dataSource和accountRepository)可能导致意外的早期初始化。
注意:与此类似的是,如果创建的Bean为
BeanPostProcessor或BeanFactoryPostProcessor,应该将方法定义为 static方法,从而防止Configuration类被过早实例化。
查找方法注入
在单例作用域的 bean 依赖于原型作用域的 bean 的情况下,通过使用 Java 配置,您可以创建CommandManager的子类,在该子类中,抽象createCommand()方法被覆盖,从而可以查找新的(原型)命令对象。
121public abstract class CommandManager {2 public Object process(Object commandState) {3 // 获取一个新实例,并初始化4 Command command = createCommand();5 command.setState(commandState);6 // 使用新实例来执行业务逻辑7 return command.execute();8 }9
10 // okay... but where is the implementation of this method?11 protected abstract Command createCommand();12}181// 被依赖的原型Bean:asyncCommand2("prototype")4public AsyncCommand asyncCommand() {5 AsyncCommand command = new AsyncCommand();6 return command;7}8
9// 依赖原型Bean的单例Bean:commandManager10public CommandManager commandManager() {12 // 返回单例Bean实例,并实现查找方法:createCommand()13 return new CommandManager() {14 protected Command createCommand() {15 return asyncCommand();16 }17 }18}
4. 导入其它配置类
与 XML 配置中的 import 标签一样,Java 配置中可以使用 @import 注解来导入其它配置类(或常规组件类)。
231public class ConfigA {3
4 5 public A a() {6 return new A();7 }8}9
10({ConfigA.class,UserService.class})12public class ConfigB {13
14 15 public B b() {16 return new B();17 }18}19
20public class UserService {22}23
如果需要导入的类数量比较多,还可以使用ImportSelector或ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口来辅助导入。
141public class Myclass implements ImportSelector {2 3 public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {4 // 返回全类名数组(注意不能返回null) 5 return new String[]{"com.yc.Test.TestDemo3"}; // 也可以这样写TestDemo3.class.getName()6 }7}8
9public class WaiterRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {10 11 public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry){12 registry.registerBeanDefinition("waiter", new RootBeanDefinition(Waiter.class));13 }14}如果想对某些配置类或Bean进行选择性导入,即在dev环境导入指定类,在test环境导入另外的类,可以使用@Profile注解,具体用法可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/ysl19910806/article/details/91646554。
注意:
使用@Import导入Bean对象时,无需对应类添加@Component组件注解。
ImportSelector通常用于简单的条件导入,而ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar用于动态注册或修改 bean 定义等更复杂的场景。
ImportSelector和ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar实现类要被@Import导入后才会生效,并且该实现类不会被注册到IOC容器中。
ImportSelector的子类
DeferredImportSelector也可以用于导入Bean对象,且在配置类的解析工作完成后才生效,但又比ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar早,主要用于条件装配场景。
5. Java和XML配置混合使用
以XML为中心
即使用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 来创建容器,注解中的配置在XML中引入,主要思路是将配置类作为一个 Bean 注册到容器中,容器会识别@Configuration注解并正确处理配置类中声明的@Bean方法。
71<beans>2 <!-- 打开注解配置开关 -->3 <context:annotation-config/>4
5 <!-- 定义配置类作为一个Bean -->6 <bean class="com.acme.AppConfig"/>7</beans>也可以使用注解扫描来进行配置类的Bean定义,因为@Configuration使用了@Component进行元注解。
41<beans>2 <!-- 配置注解扫描(隐式打开注解配置开关) -->3 <context:component-scan base-package="com.acme"/>4</beans>
以注解为中心的配置
即使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 来创建容器,通过在@Configuration类上使用@ImportResource注解来导入外部XML配置文件。
181("classpath:/com/acme/properties-config.xml")3public class AppConfig {4
5 ("${jdbc.url}")6 private String url;7
8 ("${jdbc.username}")9 private String username;10
11 ("${jdbc.password}")12 private String password;13
14 15 public DataSource dataSource() {16 return new DriverManagerDataSource(url, username, password);17 }18}41<!-- properties-config.xml -->2<beans>3 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:/com/acme/jdbc.properties"/>4</beans>
6. 关于在组件中定义Bean的说明
可以在 @Component 中使用 @Bean 注解来定义其它的 Bean,但这些Bean是有限制的。
311public class FactoryMethodComponent {3 private static int i;4
5 6 ("public")7 public TestBean publicInstance() {8 return new TestBean("publicInstance");9 }10
11 // use of a custom qualifier and autowiring of method parameters12 13 protected TestBean protectedInstance( ("public") TestBean spouse, 14 ("#{privateInstance.age}") String country) {15 TestBean tb = new TestBean("protectedInstance", 1);16 tb.setSpouse(spouse);17 tb.setCountry(country);18 return tb;19 }20
21 22 private TestBean privateInstance() {23 return new TestBean("privateInstance", i++);24 }25
26 27 28 public TestBean requestScopedInstance() {29 return new TestBean("requestScopedInstance", 3);30 }31}常规 Spring 组件中的@Bean方法的处理方式与 Spring @Configuration类中相应方法的处理方式不同。不同之处在于,CGLIB 并未增强@Component类来拦截方法和字段的调用。 CGLIB 代理是调用@Configuration类中@Bean方法中的方法或字段中的字段的方法,用于创建 Bean 元数据引用以协作对象。此类方法不是用普通的 Java 语义调用的,而是通过容器进行的,以提供通常的生命周期 Management 和 Spring bean 的代理,即使通过编程调用@Bean方法引用其他 bean 时也是如此。相反,在普通@Component类内的@Bean方法中调用方法或字段具有标准 Java 语义,而无需特殊的 CGLIB 处理或其他约束。
您可以将@Bean方法声明为static,从而允许在不将其包含的配置类创建为实例的情况下调用它们。在定义后处理器 Bean(例如,类型BeanFactoryPostProcessor或BeanPostProcessor)时,这特别有意义,因为此类 Bean 在容器生命周期的早期进行了初始化,并且应避免在那时触发配置的其他部分。
由于技术限制,对静态@Bean方法的调用永远不会被容器拦截,即使在@Configuration类中也是如此(如本节前面所述),由于技术限制:CGLIB 子类只能覆盖非静态方法。因此,直接调用另一个@Bean方法具有标准的 Java 语义,从而导致直接从工厂方法本身直接返回一个独立的实例。
@Bean方法的 Java 语言可见性不会对 Spring 容器中的最终 bean 定义产生直接影响。您可以随意声明自己的工厂方法,以适合非@Configuration类,也可以随处声明静态方法。但是,@Configuration类中的常规@Bean方法必须是可重写的—即,不得将它们声明为private或final。
还可以在给定组件或配置类的 Base Class 上以及在由组件或配置类实现的接口中声明的 Java 8 默认方法上找到@Bean方法。这为组合复杂的配置安排提供了很大的灵 Active,从 Spring 4.2 开始,通过 Java 8 默认方法甚至可以实现多重继承。
最后,单个类可以为同一个 bean 保留多个@Bean方法,这取决于在运行时可用的依赖关系,从而可以使用多个工厂方法。这与在其他配置方案中选择“最贪婪”的构造函数或工厂方法的算法相同:在构造时将选择具有最大可满足依赖关系数量的变量,类似于容器在多个@Autowired构造函数之间进行选择的方式。
您还可以声明类型为InjectionPoint(或其更具体的子类:DependencyDescriptor)的工厂方法参数,以访问触发当前 bean 创建的请求注入点。注意,这仅适用于实际创建 bean 实例,而不适用于注入现有实例。因此,此功能对原型范围的 bean 最有意义。
81public class FactoryMethodComponent {3
4 ("prototype")5 public TestBean prototypeInstance(InjectionPoint injectionPoint) {6 return new TestBean("prototypeInstance for " + injectionPoint.getMember());7 }8}
第七节 其它补充
Environment接口用来表示整个应用运行时的环境,是当前Bean集合及相关属性在容器中的一个抽象,定义了下面两个重要的概念。
1. Profile
Profile用于控制哪些Bean被注册,哪些Bean不被注册,只有处于活动状态的 Bean 才会被注册。@Profile 是 Spring 为我们提供的可以根据当前环境,动态的激活和切换一系列组件的功能。
为Bean配置环境
@Profile 注解可以作用于配置类或方法之上,表示只有对应的环境被激活时,被注解的Bean才会被注册到Spring容器。
251("development")3public class StandaloneDataConfig {4
5 6 public DataSource dataSource() {7 return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()8 .setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.HSQL)9 .addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/schema.sql")10 .addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/test-data.sql")11 .build();12 }13}14
15("production")17public class JndiDataConfig {18
19 (destroyMethod="")20 public DataSource dataSource() throws Exception {21 Context ctx = new InitialContext();22 return (DataSource) ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/jdbc/datasource");23 }24}25
201public class AppConfig {3
4 ("dataSource")5 ("development")6 public DataSource standaloneDataSource() {7 return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()8 .setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.HSQL)9 .addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/schema.sql")10 .addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/test-data.sql")11 .build();12 }13
14 ("dataSource")15 ("production")16 public DataSource jndiDataSource() throws Exception {17 Context ctx = new InitialContext();18 return (DataSource) ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/jdbc/datasource");19 }20}提示
可以使用一些基本运算符来配置Bean的环境。如
production & (us-east | eu-central)。可以同时配置多个环境。如
@Profile({"p1", "!p2"})表示在p1活动状态或p2未活动状态进行注册。如果 @Profile 注解作用于同名的@Bean方法(方法重载)之上,则它们之间的配置最好相同。
在XML配置中,可以使用 beans 标签的profile属性来配置Bean的环境,但可能会有一些限制。
111<beans profile="development"2 xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"5 xsi:schemaLocation="...">6
7 <jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource">8 <jdbc:script location="classpath:com/bank/config/sql/schema.sql"/>9 <jdbc:script location="classpath:com/bank/config/sql/test-data.sql"/>10 </jdbc:embedded-database>11</beans>
激活环境
我们在启动容器时,需要指定激活的环境,否则会抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException。最直接的方法是通过 Environment API 以编程方式进行配置。
41AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();2ctx.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("profile1", "profile2");3ctx.register(SomeConfig.class, StandaloneDataConfig.class, JndiDataConfig.class);4ctx.refresh();当然,也可以使用声明式的方式,通过系统环境变量、JVM系统属性等方式设置 spring.profiles.active 属性的值。
11-Dspring.profiles.active="profile1,profile2"
在特定环境,如WEB开发中也可以设置web.xml中的servlet 上下文参数,或测试环境中,通过 @ActiveProfiles 注解来声明。
默认环境
当spring.profiles.active没有被设置时,那么Spring会根据spring.profiles.default属性的对应值来进行Profile进行激活。spring.profiles.default属性的默认值为 default,可以使用setDefaultProfiles()方法或spring.profiles.default属性来修改。
121("default")3public class DefaultDataConfig {4
5 6 public DataSource dataSource() {7 return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()8 .setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.HSQL)9 .addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/schema.sql")10 .build();11 }12}
2. @PropertySource
Property 表示当前环境中的属性配置,属性可能来源于properties文件、JVM properties、system环境变量、JNDI、servlet context parameters上下文参数、专门的properties对象,Maps等。@PropertySource 注解用于加载指定的属性文件(properties/xml/yml)到 Spring 的 Environment 中。
从环境中取出属性
我们可以使用${}或env.getProperty("")从 Environment 中取出这些值。
141("classpath:/com/${my.placeholder:default/path}/app.properties")3public class AppConfig {4
5 6 Environment env;7
8 9 public TestBean testBean() {10 TestBean testBean = new TestBean();11 testBean.setName(env.getProperty("testbean.name"));12 return testBean;13 }14}
与@Value组合使用
@PropertySource与@Value组合使用,可以将自定义属性文件中的属性变量值注入到当前类的使用@Value注解的成员变量中。
221(value = {"demo/props/demo.properties"})3public class ReadByPropertySourceAndValue {4
5 ("${demo.name}")6 private String name;7
8 ("${demo.sex}")9 private int sex;10
11 ("${demo.type}")12 private String type;13
14 15 public String toString() {16 return "ReadByPropertySourceAndValue{" +17 "name='" + name + '\'' +18 ", sex=" + sex +19 ", type='" + type + '\'' +20 '}';21 }22}
与@ConfigurationProperties组合使用(SpringBoot)
和 @ConfigurationProperties 组合使用,可以将属性文件与一个Java类绑定,将属性文件中的变量值注入到该Java类的成员变量中。
441(value = {"demo/props/demo.properties"})3(prefix = "demo")4public class ReadByPropertySourceAndConfProperties {5
6 private String name;7
8 private int sex;9
10 private String type;11
12 public void setName(String name) {13 this.name = name;14 }15
16 public void setSex(int sex) {17 this.sex = sex;18 }19
20 public void setType(String type) {21 this.type = type;22 }23
24 public String getName() {25 return name;26 }27
28 public int getSex() {29 return sex;30 }31
32 public String getType() {33 return type;34 }35
36 37 public String toString() {38 return "ReadByPropertySourceAndConfProperties{" +39 "name='" + name + '\'' +40 ", sex=" + sex +41 ", type='" + type + '\'' +42 '}';43 }44}
3. 标准和自定义事件
ApplicationContext中的事件处理是通过ApplicationEvent类和ApplicationListener接口提供的。如果将实现ApplicationListener接口的 bean 部署到上下文中,则每次将ApplicationEvent发布到ApplicationContext时,都会通知该 bean。本质上,这是标准的 Observer 设计模式。 下表描述了 Spring 提供的标准事件:
| Event | Explanation |
|---|---|
ContextRefreshedEvent | 在初始化或刷新ApplicationContext时发布(例如,通过使用ConfigurableApplicationContext接口上的refresh()方法)。在这里,“已初始化”是指所有 Bean 都已加载,检测到并激活了后处理器 Bean,已预先实例化单例,并且已准备好使用ApplicationContext对象。只要尚未关闭上下文,只要选定的ApplicationContext实际上支持这种“热”刷新,就可以多次触发刷新。例如,XmlWebApplicationContext支持热刷新,但GenericApplicationContext不支持。 |
ContextStartedEvent | 在ConfigurableApplicationContext界面上使用start()方法启动ApplicationContext时发布。在这里,“启动”是指所有Lifecycle bean 都收到一个明确的启动 signal。通常,此 signal 用于在显式停止后重新启动 Bean,但也可以用于启动尚未配置为自动启动的组件(例如,尚未在初始化时启动的组件)。 |
ContextStoppedEvent | 在ConfigurableApplicationContext接口上使用stop()方法停止ApplicationContext时发布。此处,“已停止”表示所有Lifecycle bean 都收到一个明确的停止 signal。停止的上下文可以通过start()调用重新启动。 |
ContextClosedEvent | 在ConfigurableApplicationContext接口上使用close()方法关闭ApplicationContext时发布。此处,“封闭”表示所有单例 bean 都被破坏。封闭的情境到了生命的尽头。无法刷新或重新启动。 |
RequestHandledEvent | 一个特定于 Web 的事件,告诉所有 Bean HTTP 请求已得到服务。请求完成后,将发布此事件。此事件仅适用于使用 Spring 的DispatcherServlet的 Web 应用程序。 |
您还可以创建和发布自己的自定义事件。以下示例显示了一个简单的类,该类扩展了 Spring 的ApplicationEventBase Class:
131public class BlackListEvent extends ApplicationEvent {2
3 private final String address;4 private final String content;5
6 public BlackListEvent(Object source, String address, String content) {7 super(source);8 this.address = address;9 this.content = content;10 }11
12 // accessor and other methods...13}要发布自定义ApplicationEvent,请在ApplicationEventPublisher上调用publishEvent()方法。通常,这是通过创建一个实现ApplicationEventPublisherAware的类并将其注册为 Spring bean 来完成的。以下示例显示了此类:
211public class EmailService implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {2
3 private List<String> blackList;4 private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;5
6 public void setBlackList(List<String> blackList) {7 this.blackList = blackList;8 }9
10 public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {11 this.publisher = publisher;12 }13
14 public void sendEmail(String address, String content) {15 if (blackList.contains(address)) {16 publisher.publishEvent(new BlackListEvent(this, address, content));17 return;18 }19 // send email...20 }21}在配置时,Spring 容器检测到EmailService实现ApplicationEventPublisherAware并自动调用setApplicationEventPublisher()。实际上,传入的参数是 Spring 容器本身。您正在通过其ApplicationEventPublisher接口与应用程序上下文进行交互。
要接收自定义ApplicationEvent,您可以创建一个实现ApplicationListener的类并将其注册为 Spring Bean。以下示例显示了此类:
121public class BlackListNotifier implements ApplicationListener<BlackListEvent> {2
3 private String notificationAddress;4
5 public void setNotificationAddress(String notificationAddress) {6 this.notificationAddress = notificationAddress;7 }8
9 public void onApplicationEvent(BlackListEvent event) {10 // notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...11 }12}注意,ApplicationListener通常用您的自定义事件的类型(上一示例中的BlackListEvent)进行参数化。这意味着onApplicationEvent()方法可以保持类型安全,从而避免了向下转换的任何需要。您可以根据需要注册任意数量的事件侦听器,但是请注意,默认情况下,事件侦听器会同步接收事件。这意味着publishEvent()方法将阻塞,直到所有侦听器都已完成对事件的处理为止。这种同步和单线程方法的一个优点是,当侦听器收到事件时,如果有可用的事务上下文,它将在发布者的事务上下文内部进行操作。
以下示例显示了用于注册和配置上述每个类的 Bean 定义:
131<bean id="emailService" class="example.EmailService">2 <property name="blackList">3 <list>4 <value>[emailprotected]</value>5 <value>[emailprotected]</value>6 <value>[emailprotected]</value>7 </list>8 </property>9</bean>10
11<bean id="blackListNotifier" class="example.BlackListNotifier">12 <property name="notificationAddress" value="[emailprotected]"/>13</bean>将所有内容放在一起,当调用emailService bean 的sendEmail()方法时,如果有任何电子邮件消息应列入黑名单,则会发布BlackListEvent类型的自定义事件。 blackListNotifier bean 注册为ApplicationListener并接收BlackListEvent,此时它可以通知适当的参与者。
Spring 的事件机制旨在在同一应用程序上下文内在 Spring bean 之间进行简单的通信。但是,对于更复杂的企业集成需求,单独维护的Spring Integration项目为构建基于众所周知的 Spring 编程模型的事件驱动的轻量级pattern-oriented体系结构提供了完整的支持。
从 Spring 4.2 开始,您可以使用EventListener注解在托管 Bean 的任何公共方法上注册事件侦听器。
131public class BlackListNotifier {2
3 private String notificationAddress;4
5 public void setNotificationAddress(String notificationAddress) {6 this.notificationAddress = notificationAddress;7 }8
9 10 public void processBlackListEvent(BlackListEvent event) {11 // notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...12 }13}方法签名再次声明其侦听的事件类型,但是这次使用灵活的名称并且没有实现特定的侦听器接口。只要实际事件类型在其实现层次结构中解析您的通用参数,也可以通过通用类型来缩小事件类型。
如果您的方法应该侦听多个事件,或者您要完全不使用任何参数来定义它,则事件类型也可以在注解本身上指定。以下示例显示了如何执行此操作:
41({ContextStartedEvent.class, ContextRefreshedEvent.class})2public void handleContextStart() {3 ...4}也可以通过使用定义SpEL expression的注解的condition属性来添加其他运行时过滤,该属性应匹配以针对特定事件实际调用该方法。
以下示例显示了仅当事件的content属性等于my-event时,才可以重写我们的通知程序以进行调用:
41(condition = "#blEvent.content == 'my-event'")2public void processBlackListEvent(BlackListEvent blEvent) {3 // notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...4}每个SpEL表达式都针对专用上下文进行评估。下表列出了可用于上下文的项目,以便您可以将它们用于条件事件处理:
| Name | Location | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Event | root object | 实际的ApplicationEvent。 | #root.event |
| Arguments array | root object | 用于调用目标的参数(作为数组)。 | #root.args[0] |
| Argument name | evaluation context | 任何方法参数的名称。如果由于某种原因名称不可用(例如,因为没有调试信息),则参数名称也可以在#a<#arg>下获得,其中#arg代表参数索引(从 0 开始)。 | #blEvent或#a0(您也可以使用#p0或#p<#arg>表示法作为别名) |
请注意,即使您的方法签名实际上引用了已发布的任意对象,#root.event也使您可以访问基础事件。
如果由于处理另一个事件而需要发布一个事件,则可以更改方法签名以返回应发布的事件,如以下示例所示:
51public ListUpdateEvent handleBlackListEvent(BlackListEvent event) {3 // notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress and4 // then publish a ListUpdateEvent...5}asynchronous listeners不支持此功能
此新方法为上述方法处理的每个BlackListEvent发布一个新的ListUpdateEvent。如果您需要发布多个事件,则可以返回Collection事件。
异步事件监听
如果希望特定的侦听器异步处理事件,则可以重用常规@Async 支持。以下示例显示了如何执行此操作:
51public void processBlackListEvent(BlackListEvent event) {4 // BlackListEvent is processed in a separate thread5}使用异步事件时,请注意以下限制:
如果事件监听器抛出Exception,则它不会传播到调用者。有关更多详细信息,请参见AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler。
此类事件侦听器无法发送答复。如果您需要发送另一个事件作为处理结果,请注入ApplicationEventPublisher以手动发送事件。
监听器调用顺序
如果需要先调用一个侦听器,则可以将@Order注解添加到方法声明中,如以下示例所示:
51public void processBlackListEvent(BlackListEvent event) {4 // notify appropriate parties via notificationAddress...5}
监听器泛型
您还可以使用泛型来进一步定义事件的结构。考虑使用EntityCreatedEvent<T>,其中T是已创建的实际实体的类型。例如,您可以创建以下侦听器定义以仅接收泛型类型为Person的EntityCreatedEvent:
41public void onPersonCreated(EntityCreatedEvent<Person> event) {3 ...4}由于类型擦除,只有在触发的事件解析了事件侦听器所依据的通用参数(即诸如class PersonCreatedEvent extends EntityCreatedEvent<Person> { … })时,此方法才起作用。
在某些情况下,如果所有事件都遵循相同的结构,这可能会变得很乏味(就像前面示例中的事件一样)。在这种情况下,您可以实现ResolvableTypeProvider以指导框架超出运行时环境提供的范围。以下事件显示了如何执行此操作:
111public class EntityCreatedEvent<T> extends ApplicationEvent implements ResolvableTypeProvider {2
3 public EntityCreatedEvent(T entity) {4 super(entity);5 }6
7 8 public ResolvableType getResolvableType() {9 return ResolvableType.forClassWithGenerics(getClass(), ResolvableType.forInstance(getSource()));10 }11}
4. 加载时编织(LoadTimeWeaver)
如果需要在将类加载到 Java 虚拟机(JVM)中时对其进行动态转换,则可使用下面方式开启加载时编织。
41public class AppConfig {4}等效的XML配置如下:
31<beans>2 <context:load-time-weaver/>3</beans>一旦为ApplicationContext配置,该ApplicationContext内的任何 bean 都可以实现LoadTimeWeaverAware,从而接收到对加载时编织器实例的引用。
5. 使用 MessageSource 进行国际化
第02章_AOP切面
AOP全称为Aspect Oriented Programming,中文译为面向切面编程。它是一种通过预编译或动态代理的方式在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态添加某种特定功能的技术,用来弥补面向对象编程(OOP)中的一些不足,它更关注于多个类之间的共同问题,如日志记录,性能统计,安全控制,事务处理,异常处理等。
下面表格列举了AOP中的一些常用概念。
| 名词 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| Joinpoint(连接点) | 可供被拦截的方法或字段 |
| Pointcut(切入点) | 想要拦截的连接点 |
| Advice(通知/增强) | 拦截之后要做的事 |
| Introduction(引介) | 一种特殊的通知,可以为现有对象添加任何接口的实现 |
| Aspect(切面) | 是切入点和通知(引介)的结合 |
| Advisors(顾问) | 一种特殊的切面,只包含一个通知(引介),是SpringAOP中独有的概念 |
| Weaving(织入) | 把切面的功能应用到业务类的过程 |
Spring框架以IOC容器为基础,引入了AspectJ相关注解和类库,实现了基于方法拦截的AOP支持,用于提供声明式企业服务,并且使用户也能够基于IOC容器做一些自定义的切面功能。
SpringAOP是纯Java实现的,采用运行期动态代理织入,不需要特殊的编译过程或控制类加载器的层次结构。如果你仅需要拦截Bean的一些方法,执行额外的逻辑,推荐你使用SpringAOP,因为这更加简单,不需要在开发和构建过程中引入 AspectJ 编译器/编织器。但如果你想拦截非Spring管理对象(如域对象)中的方法,或者想拦截字段,那么请参考AspectJ的使用。
第一节 定义切面
切面是切入点和通知(引介)的结合,你可以通过AspectJ语言的相关注解声明和配置一个切面。
1. 导入相关Jar包
首先导入SpringAOP开发过程中需要使用的jar包spring-aop.jar和aspectjweaver.jar等。
121<!--SpringAOP核心Jar包:包含AOP支持和spring-beans/spring-core两个子包,并集成了aopalliance所定义的注解和异常-->2<dependency>3 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>4 <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>5</dependency>6
7<!--AspectJ依赖包:AspectJ所定义的AOP注解和切入点表达式支持等-->8<dependency>9 <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>10 <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>11</dependency>12
2. 使用注解配置切面
Spring基于AspectJ相关注解提供AOP注解配置,默认情况下,Spring 不会检测AspectJ相关注解,需要通过Java配置或XML配置开启。
开启注解AOP支持
如果你是基于Java配置的项目,可以在配置类上加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解开启注解AOP支持。
51 3public class AppConfig {4}5
如果你是基于XML配置的项目,可以在Spring配置文件中加入<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>元素开启注解AOP支持。
131 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"5 xsi:schemaLocation="6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">8
9 <!-- 开启注解AOP支持 -->10 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>11
12</beans>13
使用@Aspect注解配置切面
注解配置开关开启后,即可通过org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect注解将Bean声明为一个切面,Spring在创建相关Bean时,会检测Bean上的AspectJ注解,并使用动态代理进行AOP配置。
81package org.xyz;2import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;3
4 // 将该Bean声明为一个切面5 6public class NotVeryUsefulAspect {7
8}注意:关于声明切面的几点注意事项
@Aspect注解不足以在 Classpath 中被自动检测,因此需要再添加一个@Component注解。
切面本身不能成为其他切面的目标,标记某个类为切面的同时,会自动从其它切面的动态代理列表排除。
3. 使用XML配置切面
使用XML方式配置AOP切面,首先需导入相关的Schema约束(参见附录中的[AOP Schema][https://www.docs4dev.com/docs/zh/spring-framework/5.1.3.RELEASE/reference/core.html#xsd-schemas-aop]),引入aop名称空间。然后,使用<aop:config>标签按顺序配置切入点、切面、通知等元素。
171 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">7
8 <!--将通知所在类配置为一个Bean,id为loggingAspect-->9 <bean id="loggingAspect" class="com.szkingdom.kfms.base.LoggingAspect"/>10 11 <!--AOP配置标签(可以存在多个)-->12 <aop:config> 13 <!--配置 loggingAspect(Bean) 作为切面-->14 <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="loggingAspect">15 </aop:aspect>16 </aop:config>17</beans>注意:<aop:config>样式的配置大量使用了 Spring 的auto-proxying机制。如果您已经通过使用BeanNameAutoProxyCreator或类似方法来使用显式自动代理,则可能会导致问题(例如未编制建议)。
第二节 声明切入点
切入点指想要拦截的方法或字段,通过切入点表达式来确定哪些连接点作为切入点。需要注意的是,Spring中仅支持方法类型的切入点。
1. 使用注解声明切入点
可以直接在通知上配置切入点表达式来声明切入点。
31// 定义一个通知 并通过切入点表达式声明切入点2("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))")3public void doSome() {}
也可以在void方法上加@Pointcut注解来定义单独的切入点,然后在通知上进行引用(注意加小括号)。
71// 定义一个切入点 2("execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))") 3private void pt1() {} 4
5// 定义一个通知 并引用定义好的切入点6("pt1()")7public void doSome() {}
2. 使用XML声明切入点
可以直接在通知配置的pointcut属性配置切入点表达式。
71<aop:config>2 <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="loggingAspect">3 <!-- 定义一个通知,直接使用 pointcut 属性配置切入点表达式-->4 <aop:before method="before01" pointcut="execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))"/>5 </aop:aspect>6</aop:config>7
但一般来说,会单独定义切入点配置元素,提供给多个通知引用。
121<aop:config>2
3 <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="loggingAspect">4 <!--事先定义切入点businessService,匹配service包下的所有方法-->5 <aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))"/>6
7 <!--在通知中引用配置的切入点businessService-->8 <aop:before pointcut-ref="businessService" method="before01"/>9 </aop:aspect>10
11</aop:config>12
3. 使用接口声明切入点
本节介绍如何通过实现接口的方式进行切入点的配置,虽然Spring5仍支持这种方式,但一般不推荐使用。
切入点接口
切入点接口org.springframework.aop.Pointcut定义如下,实现该接口,即可定义一个切入点,用于定义想要被拦截的方法。
51public interface Pointcut {2 ClassFilter getClassFilter();3 MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();4}5
切入点接口又分为ClassFilter和MethodMatcher两个子接口,分别用于类匹配和方法匹配,定义如下。
181public interface ClassFilter {2 // 检测是否匹配某个类3 boolean matches(Class clazz);4}5
6
7public interface MethodMatcher {8 // 检测是否匹配目标类上的指定方法9 boolean matches(Method m, Class targetClass);10
11 // 表示该切入点是否为动态切入点(ture-动态切入点,false-静态切入点)12 boolean isRuntime();13 14 // 如果前两个方法都返回true,那么将会调用该方法,使用参数进行动态切入点匹配15 boolean matches(Method m, Class targetClass, Object[] args);16}17
18
静态切入点和动态切入点
静态切入点是基于方法和目标类的,不能考虑方法的参数,从而只在首次调用方法时评估一次静态切入点并进行缓存。最常见的是使用元数据属性进行匹配的元数据驱动切入点。
动态切入点在静态切入点的基础上考虑了方法参数值,这意味着在每次调用方法时都需要根据方法参数评估切入点,有一定性能损耗。常见的动态切入点有控制流切入点
org.springframework.aop.support.ControlFlowPointcut。
AspectJ表达式切入点
从Spring2.0开始,你可以使用org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJExpressionPointcut接口来定义一个AspectJ表达式切入点,切入点表达式的具体用法,请参考前面章节。
61// 定义AspectJ表达式切入点2AspectJExpressionPointcut cut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();3
4// 设置AspectJ表达式5cut.setExpression("execution( int cn.hncu.xmlImpl.aspectj.Person.run())");6
正则表达式切入点
正则表达式切入点是一种常用的静态切入点,基于JDK正则表达式的实现类为JdkRegexpMethodPointcut,示例如下。
91<bean id="settersAndAbsquatulatePointcut" class="org.springframework.aop.support.JdkRegexpMethodPointcut">2 <property name="patterns">3 <!--正则表达式列表,其中任意一个匹配则为true-->4 <list>5 <value>.*set.*</value>6 <value>.*absquatulate</value>7 </list>8 </property>9</bean>Spring 提供了一个名为RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor的顾问类封装了切入点和通知,简化了使用。
141<bean id="settersAndAbsquatulateAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor">2 <!--顾问关联的通知/拦截器-->3 <property name="advice">4 <ref bean="beanNameOfAopAllianceInterceptor"/>5 </property>6 7 <!--patterns属性:用于创建正则表达式切入点-->8 <property name="patterns">9 <list>10 <value>.*set.*</value>11 <value>.*absquatulate</value>12 </list>13 </property>14</bean>
第三节 制作通知
通知指拦截后要执行的逻辑,一般与切入点表达式关联使用。Spring支持的通知类型有:前置通知(Before Advice)、后置通知(AfterReturning Advice)、异常通知(AfterThrowing Advice)、最终通知(After Advice)和环绕通知(Around Advice)。
1. 前置通知
注解方式
前置通知在切入点方法执行之前执行,可以使用@Before注解标识切面中的某个方法为前置通知。
181import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;2import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;3
4public class BeforeExample {6 // 前置通知7 // 直接定义切入点表达式8 ("execution(* com.xyz.myapp.dao.*.*(..))")9 public void doAccessCheck01() {10 }11 12 // 前置通知13 // 引用定义好的切入点表达式)14 ("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.dataAccessOperation()")15 public void doAccessCheck02() {16 }17}18
XML方式
61<aop:aspect id="beforeExample" ref="loggingAspect">2 <!--前置通知-->3 <aop:before method="doAccessCheck" pointcut-ref="dataAccessOperation"/>4
5</aop:aspect>6
接口方式
也可以通过实现org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice接口定义一个前置通知。前置通知允许在连接点方法调用前执行一些自定义逻辑,但不能更改返回值,如果前置通知出现异常,则会传播回拦截器链。
201// 接口定义2public interface MethodBeforeAdvice extends BeforeAdvice {3
4 void before(Method m, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable;5}6
7// 使用示例8public class CountingBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {9
10 private int count;11
12 public void before(Method m, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {13 ++count;14 }15
16 public int getCount() {17 return count;18 }19}20
2. 后置通知(正常返回)
注解方式
后置通知在切入点方法执行之后执行,可以使用@AfterReturning注解标识切面中的某个方法为后置通知。如果想在后置通知中获取切入点方法返回的实际值,可以使用注解的returning属性指定一个参数名称接收返回值,并且限制仅匹配参数类型与业务方法返回值类型兼容的方法。
141import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;2import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;3
4public class AfterReturningExample {6 // 后置通知7 // 使用returning属性指定参数名称用于接收返回值8 (9 pointcut="com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.dataAccessOperation()",10 returning="retVal")11 public void doAccessCheck04(Object retVal) {12 }13}14
XML方式
61<aop:aspect id="afterReturningExample" ref="aBean">2 <!--将切面的 doAccessCheck 方法配置为后置通知,拦截 dataAccessOperation 表达式匹配的方法,并将方法的返回值传递给通知的retVal参数-->3 <aop:after-returning method="doAccessCheck" pointcut-ref="dataAccessOperation" returning="retVal"/>4
5</aop:aspect>6
doAccessCheck方法必须声明一个名为retVal的参数,该参数的类型以与@AfterReturning相同的方式约束匹配。
31public void doAccessCheck(Object retVal){2}3
接口方式
通过实现org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice接口定义一个后置通知。后置通知可以访问返回值(不能被修改),方法的参数和目标对象等运行时信息。
231// 接口定义2public interface AfterReturningAdvice extends Advice {3
4 void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method m, Object[] args, Object target)5 throws Throwable;6}7
8//使用示例9public class CountingAfterReturningAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {10
11 private int count;12
13 public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method m, Object[] args, Object target)14 throws Throwable {15 ++count;16 }17
18 public int getCount() {19 return count;20 }21}22
23
3. 异常通知
注解方式
异常通知在切入点方法抛出异常时执行(与catch代码块执行时机类似),可以使用@AfterThrowing注解标识切面中的某个方法为异常通知。通常,我们只想对部分特殊的异常进行拦截,并且希望能够在通知中获取异常信息,这可以使用throwing属性来指定一个参数名称接收抛出的异常。
141import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;2import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;3
4public class AfterThrowingExample {6 // 异常通知7 // 使用 throwing 属性指定参数名称用于接收抛出的异常8 (9 pointcut="com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.dataAccessOperation()",10 throwing="ex")11 public void doRecoveryActions(DataAccessException ex) {12 }13}14
XML方式
91<aop:aspect id="afterThrowingExample" ref="aBean">2
3 <!--将切面的 doRecoveryActions 方法配置为异常通知,拦截 dataAccessOperation 表达式匹配的方法,并将引发的异常传递给通知的dataAccessEx参数-->4 <aop:after-throwing method="doRecoveryActions" pointcut-ref="dataAccessOperation" throwing="dataAccessEx" />5
6 ...7
8</aop:aspect>9
doRecoveryActions方法必须声明一个名为dataAccessEx的参数,该参数的类型以与@AfterThrowing相同的方式约束匹配。
31public void doRecoveryActions(DataAccessException dataAccessEx){2}3
接口方式
通过实现org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice接口定义一个异常通知。由于为了兼容类型化参数,因此ThrowsAdvice接口中无任何抽象方法。
51public interface ThrowsAdvice extends AfterAdvice {2
3 // afterThrowing([Method, args, target], subclassOfThrowable)4}5
你可以定义一个或四个参数的afterThrowing方法来适应不同的处理场景,并支持定义在一个类中,如下示例。
131// 一个异常通知类,分别处理RemoteException和ServletException异常2public static class CombinedThrowsAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice {3
4 // 处理RemoteException异常5 public void afterThrowing(RemoteException ex) throws Throwable {6 7 }8
9 // 处理ServletException异常,并接入运行时信息10 public void afterThrowing(Method m, Object[] args, Object target, ServletException ex) {11 12 }13}如果异常通知本身引发异常,则它将覆盖原始异常,通常重写为 RuntimeException 类型,与任何方法签名都兼容。如果需要重写为受检异常,则必须与目标方法的已声明异常相匹配。
4. 最终通知
注解方式
最终通知在方法执行完毕退出时执行(与finally代码块执行时机类似),可以使用@After注解标识切面中的某个方法为最终通知。
111import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;2import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;3
4public class AfterFinallyExample {6 // 最终通知7 ("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.dataAccessOperation()")8 public void doReleaseLock() {9 }10}11
XML方式
61<aop:aspect id="afterFinallyExample" ref="aBean">2 <!--将切面的 doReleaseLock 方法配置为最终通知,拦截 dataAccessOperation 表达式匹配的方法-->3 <aop:after method="doReleaseLock" pointcut-ref="dataAccessOperation"/>4
5</aop:aspect>6
5. 环绕通知
注解方式
环绕通知在方法执行的四个阶段都可以添加额外逻辑,相当于前四种通知的集合,可以使用@Around注解标识切面中的某个方法为环绕通知。通常用于需要以线程安全的方式在方法执行之前和之后共享状态的情形下使用,例如启动和停止计时器。如果前四种通知能够满足你的需求,那么尽量不要使用环绕通知。
环绕通知的第一个参数必须为ProceedingJoinPoint类型,通过调用其Object proceed()或Object proceed(Object[] var1)方法,即可执行原业务逻辑,该方法可以在通知中被执行一次,多次甚至0次!
环绕通知的返回值类型应该与业务方法的返回值类型一致或是其子类,否则将会出现类型转换异常。
201import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;2import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;3import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;4
5public class AroundExample {7 // 环绕通知8 ("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService()")9 public Object doBasicProfiling(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {10 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();11 12 // 执行业务方法13 Object retVal = pjp.proceed();14 15 System.out.println("方法总耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-begin)+"ms");16 17 return retVal;18 }19}20
XML方式
61<aop:aspect id="aroundExample" ref="aBean">2 <!--将切面的 doBasicProfiling 方法配置为环绕通知,拦截 businessService 表达式匹配的方法-->3 <aop:around method="doBasicProfiling" pointcut-ref="businessService" />4
5</aop:aspect>6 与注解配置类似,环绕通知的第一个参数也必须是ProceedingJoinPoint类型。
71public Object doBasicProfiling(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {2 // start stopwatch3 Object retVal = pjp.proceed();4 // stop stopwatch5 return retVal;6}7
接口方式
通过实现org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor接口定义一个环绕通知,并通过MethodInvocation来获取运行时相关信息和进行连接点方法的调用。
171// 接口定义2public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {3
4 Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;5}6
7// 使用示例8public class DebugInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {9
10 public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {11 System.out.println("Before: invocation=[" + invocation + "]");12 Object rval = invocation.proceed();13 System.out.println("Invocation returned");14 return rval;15 }16}17
第四节 切入点详解
1. 切入点指示符
切入点表达式有多种类型,通过不同的切入点指示符(PCD)来区分,Spring支持以下几种AspectJ定义的切入点指示符。
execution:用于匹配方法执行的连接点。这是使用 Spring AOP 时要使用的主要切入点指示符。within:将匹配限制为某些类型内的连接点(使用 Spring AOP 时,在匹配类型内声明的方法的执行)。this:将匹配限制为连接点(使用 Spring AOP 时方法的执行),其中 bean 引用(Spring AOP 代理)是给定类型的实例。target:将目标对象(正在代理的应用程序对象)是给定类型的实例的连接点(使用 Spring AOP 时,方法的执行)限制为匹配。args:将参数限制为给定类型的实例的连接点(使用 Spring AOP 时方法的执行)限制匹配。@target:将执行对象的类具有给定类型的注解的连接点(使用 Spring AOP 时,方法的执行)限制为匹配。@args:限制匹配的连接点(使用 Spring AOP 时方法的执行),其中传递的实际参数的运行时类型具有给定类型的 注解。@within:将匹配限制为具有给定注解的类型内的连接点(使用 Spring AOP 时,使用给定注解的类型中声明的方法的执行)。@annotation:将匹配限制为连接点的主题(在 Spring AOP 中正在执行的方法)具有给定注解的连接点。
除此之外,Spring基于自身特性,扩展了一种附加指示符bean,其格式为bean(idOrNameOfBean),并且也支持*通配符和切入点表达式的组合运算。
扩展:完整AspectJ语言支持的其它切入点指示符
完整的 AspectJ 切入点语言还支持 call,get,set,preinitialization,staticinitialization,initialization,handler,adviceexecution,withincode,cflow,cflowbelow,if,@this和@withincode指示符,但你不能在SpringAOP中使用它们,否则会抛出IllegalArgumentException。
2. 切入点表达式
SpringAOP用户最常用的切入点指示符为execution,其切入点表达式的格式如下:
11execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)| 模式 | 是否必须 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| modifiers-pattern(修饰符模式) | 匹配指定的修饰符类型 | |
| ret-type-pattern(返回类型模式) | 是 | 匹配指定的返回值类型 |
| declaring-type-pattern(声明类型模式) | 匹配指定的包名和类名 | |
| name-pattern(名称模式) | 是 | 匹配指定的方法名称 |
| param-pattern(参数模式) | 是 | 匹配指定的参数个数和类型 |
| throws-pattern(异常类型模式) | 匹配指定的异常类型 |
下面是一些切入点表达式的示例。
441// 匹配所有的public方法。2// 注意:(..)匹配任意参数和类型的方法;(*)匹配任意类型的单参数方法; 3// (*,String)匹配第二个参数为String的双参数方法;()匹配不带参数的方法。4execution(public * *(..)) 5
6// 匹配所有set开头的方法7execution(* set*(..)) 8
9// 匹配com.xyz.service.AccountService类中的所有方法10execution(* com.xyz.service.AccountService.*(..)) 11
12// 匹配com.xyz.service包下的所有方法,也可使用 within(com.xyz.service.*)13execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..)) 14
15// 匹配com.xyz.service包及其子包下的所有方法,也可以使用 within(com.xyz.service..*)16execution(* com.xyz.service..*.*(..)) 17
18// 匹配名称为tradeService的Bean中所有方法19bean(tradeService)20
21// 匹配名称以Service结尾的Bean中所有方法22bean(*Service)23
24// 匹配代理实现AccountService接口的所有方法25this(com.xyz.service.AccountService)26
27// 匹配目标对象实现AccountService接口的所有方法28target(com.xyz.service.AccountService)29
30// 匹配运行时传递的参数为Serializable的单参数方法。注意与 execution(* *(java.io.Serializable)) 进行区分,如果运行时传递的参数为Serializable,则匹配前者,如果方法签名声明单个类型为Serializable的参数,则匹配后者31args(java.io.Serializable)32
33// 匹配带@Transactional注解的所有方法34(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)35
36// 匹配目标对象带@Transactional注解的所有方法37(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)38
39// 匹配目标对象的声明类型具有@Transactional注解的所有方法40(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)41
42// 匹配单个参数且传递的参数的运行时类型具有@Classified注解的所有方法43(com.xyz.security.Classified)44
使用切入点表达式的一些建议
this、target和args通常以绑定形式使用,@target、@within、@annotation和@args也可以以绑定形式使用。
AspectJ会在编译期间对切入点进行DNF(析取范式)重写处理,并且对切入点的组件进行排序,以优化匹配性能。
指示符可分为kinded(execution/get/set/call/handler), scoping(within/withincode)和contextual(this/target/@annotation)三类,好的切入点表达式应至少包含前两类,否则由于额外的分析和处理,很有可能会影响编织性能。
3. 表达式的组合运算
你可以使用&&, ||和!对切入点表达式进行组合,最佳实践是从较小的命名组件中构建更复杂的切入点表达式,如下例所示。
121// 匹配任何公共方法的执行2("execution(public * *(..))")3private void anyPublicOperation() {}4
5// 匹配trading包及其子包下所有类的所有方法6("within(com.xyz.someapp.trading..*)")7private void inTrading() {} 8
9// 匹配trading包及其子包下所有类的所有公共方法10("anyPublicOperation() && inTrading()")11private void tradingOperation() {} 12
接口方式同样支持切入点的组合运算,实现org.springframework.aop.support.ComposablePointcut接口定义一个组合切入点,使用union和intersection等方法即可和其它切入点、类或方法进行组合运算。
4. 共享切入点表达式
对于一些常用的切入点表达式,可以单独定义一个切面来进行存放,只需将@Pointcut注解所在的方法声明为public方法即可。
281package com.xyz.someapp;2
3import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;4import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;5
6public class SystemArchitecture {8 // com.xyz.someapp.web包及其子包下所有类中的所有方法9 ("within(com.xyz.someapp.web..*)")10 public void inWebLayer() {}11
12 // com.xyz.someapp.service包及其子包下所有类中的所有方法13 ("within(com.xyz.someapp.service..*)")14 public void inServiceLayer() {}15
16 // com.xyz.someapp.dao包及其子包下所有类中的所有方法17 ("within(com.xyz.someapp.dao..*)")18 public void inDataAccessLayer() {}19
20 // 包及其子包下的类中的所有方法21 ("execution(* com.xyz.someapp..service.*.*(..))")22 public void businessService() {}23
24 // com.xyz.someapp.dao包下所有类中的所有方法25 ("execution(* com.xyz.someapp.dao.*.*(..))")26 public void dataAccessOperation() {}27}28
在XML中可以将切入点表达式定义在切面配置之外,提供给多个切面使用。
51<aop:config>2 <!--定义一个顶级切入点businessService,匹配service包下的所有方法-->3 <aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))"/>4
5</aop:config>还支持在XML方式的切入点表达式配置中直接引用注解方式配置好的切入点。
61<aop:config>2 <!--在XML中引用SystemArchitecture类中写好的切入点-->3 <aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService()"/>4
5</aop:config>6
第五节 通知详解
1. 访问连接点
任何类型的通知都可以将第一个参数声明为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型,用于获取当前连接点对象,从而获取更多信息。
121// 获取方法参数2Object[] getArgs()3
4// 获取代理对象5Object getThis()6
7// 获取目标对象8Object getTarget()9
10// 获取通知使用的方法的签名11Signature getSignature()12
2. 绑定参数
如果需要在通知中使用方法实参,可使用切入点标识符args通过参数名称进行绑定,在调用通知时会将相应参数的值作为参数值传递。
51// args(account,..)将限制匹配第一个参数类型为Account的方法,并且将方法的account参数传递给通知。2("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.dataAccessOperation() && args(account,..)")3public void validateAccount(Account account) {4}5 此外,还可以通过切入点的方式传递参数。当切入点Account对象值与连接点匹配时,该切入点“提供”,然后从通知中引用命名切入点。
81("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.dataAccessOperation() && args(account,..)")2private void accountDataAccessOperation(Account account) {}3
4("accountDataAccessOperation(account)")5public void validateAccount(Account account) {6}7
8
代理对象(this),目标对象(target)和注解(@within,@target,@annotation和@args)都可以以类似的方式绑定。如下示例展示了如何匹配带@Auditable注解的方法,并获取注解中的AuditCode值。
131// @Auditable注解的定义2(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)3(ElementType.METHOD)4public @interface Auditable {5 AuditCode value();6}7
8// 匹配带@Auditable注解的方法,并将方法的Auditable注解传递给通知9("com.xyz.lib.Pointcuts.anyPublicMethod() && @annotation(auditable)")10public void audit(Auditable auditable) {11 AuditCode code = auditable.value();12}13
此外,基于XML方式的AOP配置也支持收集连接点上下文。例如,以下切入点收集this对象作为连接点上下文,并将其传递给通知。
121<aop:config>2
3 <aop:aspect id="myAspect" ref="loggingAspect">4 <!--定义一个切入点businessService,匹配service包下的所有方法,同时收集上下文中的this对象-->5 <aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..)) and this(service)"/>6
7 <aop:before pointcut-ref="businessService" method="before01"/>8
9 </aop:aspect>10
11</aop:config>12
注意,在声明通知时,需要通过包含匹配名称的参数来接收收集的连接点上下文,如下所示。
31// 使用service参数来接收传递的上下文2public void before01(Object service) {3}说明:
XML 文档中的&&很尴尬,因此可以分别使用and,or和not关键字代替&&,||和!。
请注意,以这种方式定义的切入点由其 XML id引用,并且不能用作命名切入点以形成复合切入点。
下面是一个参数使用示例。有一个业务代码,需要对其进行拦截。
161package x.y.service;2
3public interface PersonService {4
5 Person getPerson(String personName, int age);6}7
8// ------------------------------------------------------------------ //9
10public class DefaultPersonService implements PersonService {11
12 public Person getPerson(String name, int age) {13 return new Person(name, age);14 }15}16
接下来是切面和通知的代码逻辑。
211package x.y;2
3import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;4import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;5
6// 切面7public class SimpleProfiler {8
9 // 环绕通知10 public Object profile(ProceedingJoinPoint call, String name, int age) throws Throwable {11 StopWatch clock = new StopWatch("Profiling for '" + name + "' and '" + age + "'");12 try {13 clock.start(call.toShortString());14 return call.proceed();15 } finally {16 clock.stop();17 System.out.println(clock.prettyPrint());18 }19 }20}21 然后对切面进行配置及一些必要的其它配置。
301<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"2 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"3 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"4 xsi:schemaLocation="5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">7
8 <!--配置服务为一个Bean-->9 <bean id="personService" class="x.y.service.DefaultPersonService"/>10
11 <!--配置通知所在类为一个Bean-->12 <bean id="profiler" class="x.y.SimpleProfiler"/>13
14 <!-- AOP配置 -->15 <aop:config>16 <!-- 切面配置 -->17 <aop:aspect ref="profiler">18 <!-- 切入点配置:拦截任意修饰符任意返回值的x.y.service.PersonService.getPerson方法,19 方法参数为String和int类型, 并且将方法的实参传递给通知方法的name和age参数 -->20 <aop:pointcut id="theExecutionOfSomePersonServiceMethod" 21 expression="execution(* x.y.service.PersonService.getPerson(String,int)) 22 and args(name, age)"/>23
24 <!--环绕通知-->25 <aop:around method="profile" pointcut-ref="theExecutionOfSomePersonServiceMethod" />26 </aop:aspect>27 </aop:config>28
29</beans>30
3. 通知参数和泛型
Spring AOP可以处理类声明和方法参数中使用的泛型。假设您具有如下通用类型:
61// 泛型类和方法(需要对指定类型进行拦截)2public interface Sample<T> {3 void sampleGenericMethod(T param);4 void sampleGenericCollectionMethod(Collection<T> param);5}6
您可以通过在要拦截方法的参数类型中键入通知参数,将方法类型的拦截限制为某些参数类型:
41// 限定仅匹配param参数为MyType类型的方法2("execution(* ..Sample+.sampleGenericMethod(*)) && args(param)")3public void beforeSampleMethod(MyType param) {4}但这种方法不适用于通用集合。因此,您不能按以下方式定义切入点:
41("execution(* ..Sample+.sampleGenericCollectionMethod(*)) && args(param)")2public void beforeSampleMethod(Collection<MyType> param) {3}4
为了使这项工作有效,我们将不得不检查集合中的每个元素,这是不合理的,因为我们也无法决定通常如何处理null值。要实现类似目的,您必须将参数键入Collection<?>并手动检查元素的类型。
4. 确定参数名称
通知调用中的参数绑定依赖于切入点表达式中使用的名称与通知及切入点方法签名中声明的参数名称的匹配。在某些情况下,无法通过Java反射获得参数名称,因此 Spring AOP 使用以下策略来确定参数名称:
优先使用
argNames属性显式指定的参数名称。通知和切入点注解都有可选的argNames属性,这些信息在运行时依然可用。61// 通过 argNames 属性指定通知的参数名称为“bean,auditable”,用于从上下文获取所需要的参数值2(value="com.xyz.lib.Pointcuts.anyPublicMethod() && target(bean) && @annotation(auditable)",3argNames="bean,auditable")4public void audit(Object bean, Auditable auditable) {5AuditCode code = auditable.value();6}如果第一个参数是JoinPoint,ProceedingJoinPoint或JoinPoint.StaticPart类型,则可以从argNames属性的值中省略参数的名称。
71// argNames列表中可以省略“jp”2(value="com.xyz.lib.Pointcuts.anyPublicMethod() && target(bean) && @annotation(auditable)",3argNames="bean,auditable")4public void audit(JoinPoint jp, Object bean, Auditable auditable) {5AuditCode code = auditable.value();6}7如果参数只有一个JoinPoint,ProceedingJoinPoint或JoinPoint.StaticPart类型的参数,则argNames属性可以省略。
51// 仅一个JoinPoint类型参数,argNames属性可以省略2("com.xyz.lib.Pointcuts.anyPublicMethod()")3public void audit(JoinPoint jp) {4}5其次通过查看类的调试信息,从局部变量表中查找。但必须注意,开启调试信息后,代码将更容易被反编译,并且“删除未使用的本地代码”等一些编译优化项将不可用。
如果没有调试信息,则会从AspectJ编译器(ajc)中查找保留的可用信息,前提是@AspectJ切面已被编译。
最后,无其他信息可用的情况下,SpringAOP会自动推断绑定变量与参数的配对。例如,如果切入点表达式中仅绑定了一个变量,并且通知方法仅接受一个参数,则配对很明显。
如果在给定可用信息的情况下变量的绑定不明确,则会抛出
AmbiguousBindingException。如果以上所有策略均失败,则抛出
IllegalArgumentException。
基于XML的AOP配置与注解一样支持完全类型化的通知,即通过名称和通知方法参数匹配切入点参数。当然,你也可以通过arg-names 属性显示指定通知方法的参数名称列表,以逗号分隔。
51<!-- 配置一个前置通知audit,指定参数名称列表为"auditable",拦截 anyPublicMethod() 匹配的方法,2 并限定匹配 auditable 参数类型所对应的注解-->3<aop:before method="audit" pointcut="com.xyz.lib.Pointcuts.anyPublicMethod() and @annotation(auditable)" 4 arg-names="auditable"/>5
5. 如何处理通知参数
前面我们提到过,我们将描述如何使用在 Spring AOP 和 AspectJ 上始终有效的参数编写proceed调用。解决方案是确保建议签名按 Sequences 绑定每个方法参数。以下示例显示了如何执行此操作:
51("execution(List<Account> find*(..)) && com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.inDataAccessLayer() && args(accountHolderNamePattern)")2public Object preProcessQueryPattern(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, String accountHolderNamePattern) throws Throwable {3 String newPattern = preProcess(accountHolderNamePattern);4 return pjp.proceed(new Object[] {newPattern});5}在许多情况下,无论如何都要进行此绑定(如上例所示)。
6. 通知的顺序
当某一切入点存在多个相同类型的通知时,SpringAOP遵循与AspectJ相同的优先级规则来确定通知执行的顺序。即前置通知先执行优先级高的,后置通知、异常通知和最终通知先执行优先级低的。优先级可以通过实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口或使用Order注解来修改。特殊情形,如果这些通知存在于同一个切面时,无法指定其之间优先级,只能考虑将这些通知合并为一个通知,或者重构为单独的切面类。
在Spring5.0及之后,相同优先级时,环绕通知会在最外层执行,以包含其他类型通知。
7. 定义新的通知类型
org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter软件包是 SPI 软件包,可在不更改核心框架的情况下添加对新的自定义通知类型的支持。自定义Advice类型的唯一限制是它必须实现org.aopalliance.aop.Advice标记接口。
第六节 AOP代理创建
1. AOP代理方式
如果要代理的目标对象实现至少一个接口,则使用 JDK 动态代理,代理了由目标类型实现的所有接口。如果目标对象未实现任何接口,则将创建 CGLIB 代理。
要强制使用 CGLIB 代理,请将<aop:config>元素的proxy-target-class属性的值设置为true,如下所示:
41<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">2 <!-- other beans defined here... -->3</aop:config>4 注意,多个<aop:config/>节在运行时会折叠到一个统一的自动代理创建器中,该创建器将应用<aop:config/>节中的任何(通常来自不同 XML bean 定义文件)指定的代理设置。这也适用于<tx:annotation-driven/>和<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>元素。也就是说,在<tx:annotation-driven/>,<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>或<aop:config/>元素上使用proxy-target-class="true"会强制对所有三个元素使用 CGLIB 代理。
注意两种代理方式的优略:
JDK代理必须实现接口,且只对public方法有效。
CGLib代理要求类和方法不能被final修饰,是可变类。
2. 配置方式创建
FactoryBean是Spring提供配置复杂Bean的方式之一,可以通过其实现类 ProxyFactoryBean 来配置所需的代理对象。
ProxyFactoryBean的属性
ProxyFactoryBean从org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyConfig继承了许多有用的属性,默认值都为false。
| 属性名 | 属性说明 |
|---|---|
| proxyTargetClass | 是否使用CGLib创建代理(CGLib将会代理目标类而非目标类的接口) |
| optimize | 是否对CGLib创建的代理应用积极的优化策略 |
| frozen | 是否禁止在创建代理后通过Advised接口更改配置 |
| exposeProxy | 是否在ThreadLocal中公开当前代理,公开后目标可以使用AopContext.currentProxy()获取 |
此外,ProxyFactoryBean本身也带有一些可配置的属性。
| 属性名 | 属性说明 |
|---|---|
| proxyInterfaces | 将代理的接口列表(String[]),如未提供,则使用CGLib代理 |
| interceptorNames | 要应用的通知、Advisor或拦截器(String[]),拦截顺序取决于列表中的顺序 |
| singleton | 是否为单例,默认为true |
ProxyFactoryBean简单示例
下面是一个使用ProxyFactoryBean配置AOP代理的示例,其中目标对象实现了一个业务接口Person,默认将会采用JDK代理方式。
291<!--目标对象-->2<bean id="personTarget" class="com.mycompany.PersonImpl">3 <property name="name" value="Tony"/>4 <property name="age" value="51"/>5</bean>6
7<!--需要配置的顾问-->8<bean id="myAdvisor" class="com.mycompany.MyAdvisor">9 <property name="someProperty" value="Custom string property value"/>10</bean>11
12<!--需要配置的拦截器-->13<bean id="debugInterceptor" class="org.springframework.aop.interceptor.DebugInterceptor">14</bean>15
16<!--代理对象-->17<bean id="person" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">18 <!--指定要代理的接口列表-->19 <property name="proxyInterfaces" value="com.mycompany.Person"/>20 <!--目标对象-->21 <property name="target" ref="personTarget"/>22 <!--通知列表(注意:这里是String类型的数组,是为了在singleton属性为false时,能够创建新的拦截器)-->23 <property name="interceptorNames">24 <list>25 <value>myAdvisor</value>26 <value>debugInterceptor</value>27 </list>28 </property>29</bean>在需要目标对象personTarget的地方,完全可以使用代理对象person来替代,并会执行额外拦截逻辑。
31<bean id="personUser" class="com.mycompany.PersonUser">2 <property name="person"><ref bean="person"/></property>3</bean>如果需要切换到CGLib代理,则可以配置
proxyTargetClass属性为true,但必须注意,目标类不能被final修饰。
隐藏目标对象
也可以将目标对象定义为匿名内部Bean进行隐藏,防止应用程序获取到未被代理的对象。
271<!--需要配置的顾问-->2<bean id="myAdvisor" class="com.mycompany.MyAdvisor">3 <property name="someProperty" value="Custom string property value"/>4</bean>5
6<!--需要配置的拦截器-->7<bean id="debugInterceptor" class="org.springframework.aop.interceptor.DebugInterceptor"/>8
9<!--代理对象-->10<bean id="person" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">11 <!--指定要代理的接口列表-->12 <property name="proxyInterfaces" value="com.mycompany.Person"/>13 <!-- 目标对象(内联) -->14 <property name="target">15 <bean class="com.mycompany.PersonImpl">16 <property name="name" value="Tony"/>17 <property name="age" value="51"/>18 </bean>19 </property>20 <!--通知列表(注意:这里是String类型的数组,是为了在singleton属性为false时,能够创建新的拦截器)-->21 <property name="interceptorNames">22 <list>23 <value>myAdvisor</value>24 <value>debugInterceptor</value>25 </list>26 </property>27</bean>
使用
global*配置全局拦截器。
141<bean id="proxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">2 <property name="target" ref="service"/>3 <property name="interceptorNames">4 <list>5 <!--引入所有以global开头的拦截器-->6 <value>global*</value>7 </list>8 </property>9</bean>10
11<!--全局拦截器-->12<bean id="global_debug" class="org.springframework.aop.interceptor.DebugInterceptor"/>13<bean id="global_performance" class="org.springframework.aop.interceptor.PerformanceMonitorInterceptor"/>14
使用Bean继承来简化配置
首先,为代理对象创建父模板,定义如下。由于配置了abstract属性为true,该Bean定义将不会被实例化,相关知识可参考SpringIOC章节介绍的Bean继承。
81<bean id="txProxyTemplate" abstract="true" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean">2 <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/>3 <property name="transactionAttributes">4 <props>5 <prop key="*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>6 </props>7 </property>8</bean>后续在创建代理对象时可通过parent指定父模板来复用一些属性。
71<bean id="myService" parent="txProxyTemplate">2 <property name="target">3 <bean class="org.springframework.samples.MyServiceImpl">4 </bean>5 </property>6</bean>7
当然,对于不合适的属性也可以选择覆盖。
141<bean id="mySpecialService" parent="txProxyTemplate">2 <property name="target">3 <bean class="org.springframework.samples.MySpecialServiceImpl">4 </bean>5 </property>6 <property name="transactionAttributes">7 <props>8 <prop key="get*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop>9 <prop key="find*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop>10 <prop key="load*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,readOnly</prop>11 <prop key="store*">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop>12 </props>13 </property>14</bean>
3. 编程方式创建
可以在代码中通过代理工厂来创建所需的AOP代理。
ProxyFactory
使用ProxyFactory可以直接创建目标对象的AOP代理,而不需要依赖IOC容器,如下示例:
121// 创建目标对象的代理工厂2ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(myBusinessInterfaceImpl);3
4// 添加一个通知/拦截器5factory.addAdvice(myMethodInterceptor);6
7// 添加一个顾问8factory.addAdvisor(myAdvisor);9
10// 获取代理对象11MyBusinessInterface tb = (MyBusinessInterface) factory.getProxy();12
如需使代理对象实现其它接口,可以添加
IntroductionInterceptionAroundAdvisor类型的顾问。
AspectJProxyFactory
除此之外,还可以通过AspectJProxyFactory创建可添加切面的AOP代理。
121// 创建目标对象的切面代理工厂2AspectJProxyFactory factory = new AspectJProxyFactory(targetObject);3
4// 添加一个切面类5factory.addAspect(SecurityManager.class);6
7// 也可以添加一个已存在的切面实例8factory.addAspect(usageTracker);9
10// 获取AOP代理对象(注意是接口类型)11MyInterfaceType proxy = factory.getProxy();12
ProxyFactory、AspectJProxyFactory和之前提到的ProxyFactoryBean都是
ProxyCreatorSupport的直接子类
4. 自动扫描创建
上面介绍的ProxyFactoryBean、ProxyFactory和AspectJProxyFactory等都是手工创建AOP代理的方式,我们还可以通过IOC容器的Bean后处理器在加载时修改Bean定义来自动创建AOP代理。
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
BeanNameAutoProxyCreator是内置的BeanPostProcessor之一,注册后会自动为名称与beanNames属性相匹配的Bean创建AOP代理,支持*通配符。
131<!--注册BeanPostProcessor:BeanNameAutoProxyCreator-->2<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator">3 <!--匹配如下名称的Bean-->4 <property name="beanNames" value="jdk*,onlyJdk"/>5 6 <!--通知或拦截器列表-->7 <property name="interceptorNames">8 <list>9 <value>myInterceptor</value>10 </list>11 </property>12</bean>13
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 是一种更通用、功能更强大的自动代理创建者,注册后会自动检测上下文中的顾问,并根据顾问的切入点和通知(拦截器)自动创建AOP代理,后续从上下文获取bean对象时,会被替换为代理对象。
191<!--注册BeanPostProcessor:DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator-->2<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"/>3
4<!--顾问1-->5<bean class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor">6 <property name="transactionInterceptor" ref="transactionInterceptor"/>7</bean>8
9<!--顾问2-->10<bean id="customAdvisor" class="com.mycompany.MyAdvisor"/>11
12<!--Bean1(如果被某个顾问匹配,则会创建AOP代理)-->13<bean id="businessObject1" class="com.mycompany.BusinessObject1">14 <!-- Properties omitted -->15</bean>16
17<!--Bean2(如果被某个顾问匹配,则会创建AOP代理)-->18<bean id="businessObject2" class="com.mycompany.BusinessObject2"/>19
注意
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator只对上下文中的顾问有效,并不会自动配置定义的通知或拦截器。
类似的后处理器还有 AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator和AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator等。
5. 修改代理对象的配置
所有用于创建AOP代理对象的类都继承了ProxyCreatorSupport,而其实现了Advised接口,因此所有的AOP代理都可以被强制转换为Advised类型。该接口包括以下方法:
231// 获取所有顾问2Advisor[] getAdvisors();3
4// 添加通知/拦截器(将会被包装为一个顾问,默认为DefaultPointcutAdvisor)5void addAdvice(Advice advice) throws AopConfigException;6void addAdvice(int pos, Advice advice) throws AopConfigException;7
8// 添加顾问9void addAdvisor(Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException;10void addAdvisor(int pos, Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException;11
12// 返回顾问的索引(拦截顺序)13int indexOf(Advisor advisor);14
15// 移除顾问16boolean removeAdvisor(Advisor advisor) throws AopConfigException;17void removeAdvisor(int index) throws AopConfigException;18
19// 替换顾问20boolean replaceAdvisor(Advisor a, Advisor b) throws AopConfigException;21
22// 是否允许修改配置(如果为true时修改,则会抛出AopConfigException)23boolean isFrozen();注意:默认情况下,即使已创建代理,也可以添加或删除顾问。但引介顾问除外,因为工厂的现有代理不会显示接口更改,你必须重新从工厂获取新的代理对象。
以下示例显示了将AOP代理强转到Advised接口并检查和处理其顾问。
161// 将AOP代理强转为Advised类型2Advised advised = (Advised) myObject;3
4// 获取所有顾问5Advisor[] advisors = advised.getAdvisors();6int oldAdvisorCount = advisors.length;7System.out.println(oldAdvisorCount + " advisors");8
9// 添加一个新的拦截器(无切入点默认拦截所有方法)10advised.addAdvice(new DebugInterceptor());11
12// 添加一个通知(切入点为mySpecialPointcut)13advised.addAdvisor(new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(mySpecialPointcut, myAdvice));14
15assertEquals("Added two advisors", oldAdvisorCount + 2, advised.getAdvisors().length);16
6. AOP代理存在问题
有下面一个普通的Java类以及通常的使用方式。
191public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {2 public void bar() {3 }4 5 public void foo() {6 // 调用自身方法bar()7 this.bar();8 }9}10
11public class Main {12 public static void main(String[] args) {13 Pojo pojo = new SimplePojo();14
15 // this is a direct method call on the 'pojo' reference16 pojo.foo();17 }18}19 再来看下使用AOP代理后的使用方式。
151public class Main {2 public static void main(String[] args) {\3 // 创建一个目标对象的ProxyFactory,并添加通知4 ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());5 factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);6 factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());7
8 // 获取代理对象9 Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();10
11 // 通过代理对象调用foo()方法12 pojo.foo();13 }14}15
这里pojo是一个代理对象,调用其foo方法时,代理可以委派给与之匹配的通知。但一旦调用链到达未被代理的实际业务对象(这里指SimplePojo的实例),执行foo方法,在其内部调用bar时,this指的是未被代理的实际业务对象,此时,将没有机会被委派到与之匹配的通知,从而使AOP代理失效。
为了避免这种情况,最好的办法是进行代码重构,以免发生自调用。但Spring也提供了一种解决方案,但这将会导致你的代码完全耦合到 Spring AOP。
121public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {2
3 public void foo() {4 // this works, but... gah!5 ((Pojo) AopContext.currentProxy()).bar();6 }7
8 public void bar() {9 // some logic...10 }11}12 最后,修改下我们的main方法,在创建代理时setExposeProxy(ture),来暴露代理对象在上下文中,这样就可以使foo()方法的自身调用bar()方法的AOP代理正常工作了。
141public class Main {2 public static void main(String[] args) {3 ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());4 factory.adddInterface(Pojo.class);5 factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());6 factory.setExposeProxy(true);7
8 Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();9
10 // this is a method call on the proxy!11 pojo.foo();12 }13}14
注意:AspectJ 没有此自调用问题,因为它不是基于代理的 AOP 框架。
第七节 其它补充
1. 引介
引介(Introduction)是一种特殊的通知,可以为现有对象添加任何接口的实现。通过使用@DeclareParents注解定义一个引介。
151// 通过 JMX 公开统计信息2public class UsageTracking {4 // 引介:声明com.xzy.myapp.service包下的所有类实现UsageTracked接口,实现类为DefaultUsageTracked5 // @DeclareParents注解必须加在接口类型变量上6 (value="com.xzy.myapp.service.*+", defaultImpl=DefaultUsageTracked.class)7 public static UsageTracked mixin;8
9 // 通知:拦截businessService中的所有方法,并传递上下文中的 usageTracked 参数给通知10 ("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService() && this(usageTracked)")11 public void recordUsage(UsageTracked usageTracked) {12 usageTracked.incrementUseCount();13 }14}15 等效的XML配置及Java代码如下。
211<aop:aspect id="usageTrackerAspect" ref="usageTracking">2
3 <!-- 定义一个引介4 types-matching:为这些指定的类实现接口5 implement-interface:实现该接口6 default-impl:接口的实现7 -->8 <aop:declare-parents types-matching="com.xzy.myapp.service.*+" implement-interface="com.xyz.myapp.service.tracking.UsageTracked"9 default-impl="com.xyz.myapp.service.tracking.DefaultUsageTracked"/>10
11 <!-- 定义一个通知recordUsage,拦截 businessService() 匹配的方法,并传递上下文 usageTracked 参数给通知 -->12 <aop:before method="recordUsage" pointcut="com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService() and this(usageTracked)"/>13
14</aop:aspect>15
16
17// 切面类usageTracking中通知对应的方法18public void recordUsage(UsageTracked usageTracked) {19 usageTracked.incrementUseCount();20}21
此外,在前面示例的通知中,服务 Bean 可以直接用作UsageTracked接口的实现来使用。
21UsageTracked usageTracked = (UsageTracked) context.getBean("myService");2
提示:
你也可以使用
IntroductionInterceptor和IntroductionAdvisor来定义引介,具体介绍请参考Spring官方文档。
2. 顾问
顾问(Advisors)可以看作是一个独立的小切面,只有一条通知,通知本身由 Bean 表示,并且必须实现Spring通知类型中描述的通知接口之一。这是SpringAOP中独有的概念,在AspectJ中没有直接等效的配置。
顾问通过<aop:advisor>标签配置,最常见的使用场景为Spring的声明式事务配置。
141<aop:config>2 <!--定义一个切入点-->3 <aop:pointcut id="businessService" expression="execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))"/>4 5 <!--配置一个顾问:引用名为tx-advice的通知和名为businessService的切入点-->6 <aop:advisor advice-ref="tx-advice" pointcut-ref="businessService" />7</aop:config>8
9<!--配置事务通知-->10<tx:advice id="tx-advice">11 <tx:attributes>12 <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>13 </tx:attributes>14</tx:advice>提示:
同切面类似的,顾问同样支持使用
pointcut属性来定义内联切入点表达式,及使用order属性配置优先级你也可以通过继承
org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor类的方式定义Advisor。
3. 目标源
目标源org.springframework.aop.TargetSource用于在AOP代理处理方法调用时获取目标对象。如果未指定目标源,则使用默认实现包装本地对象,每次调用都会返回相同的目标。
使用目标源时,目标对象通常是原型Bean,这样,Spring才可以在需要的时候创建一个新对象。
可热交换目标源
使用可热交换目标源org.springframework.aop.target.HotSwappableTargetSource创建的AOP代理允许对目标对象进行替换。
131<!--目标对象-->2<bean id="initialTarget" class="mycompany.OldTarget"/>3
4<!--目标对象的可热交换目标源-->5<bean id="swapper" class="org.springframework.aop.target.HotSwappableTargetSource">6 <constructor-arg ref="initialTarget"/>7</bean>8
9<!--使用可热交换目标源创建AOP代理-->10<bean id="swappable" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">11 <property name="targetSource" ref="swapper"/>12</bean>13
您可以使用 HotSwappableTargetSource 上的swap()方法更改目标,如以下示例所示。该操作是线程安全的,并且会立即生效。
61// 获取可替换目标对象的代理对象2HotSwappableTargetSource swapper = (HotSwappableTargetSource) beanFactory.getBean("swapper");3
4// 替换目标对象为新目标对象5Object oldTarget = swapper.swap(newTarget);6
池目标源
池目标源维护了业务Bean的实例池,基于Commons Pool 2.2提供了默认实现CommonsPool2TargetSource,导入commons-pool.jar包后即可使用。
171<!--业务Bean(注意必须为原型Bean)-->2<bean id="businessObjectTarget" class="com.mycompany.MyBusinessObject" scope="prototype">3</bean>4
5<!--业务Bean的池目标源-->6<bean id="poolTargetSource" class="org.springframework.aop.target.CommonsPool2TargetSource">7 <property name="targetBeanName" value="businessObjectTarget"/>8 <!--maxSize:必须参数,池最大容量为25-->9 <property name="maxSize" value="25"/>10</bean>11
12<!--使用池目标源创建AOP代理-->13<bean id="businessObject" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">14 <property name="targetSource" ref="poolTargetSource"/>15 <property name="interceptorNames" value="myInterceptor"/>16</bean>17
注意:
Spring还支持Commons Pool 1.5,但从 Spring Framework 4.2 开始不推荐使用。
你可以继承
org.springframework.aop.target.AbstractPoolingTargetSource支持其它池化技术。
你可以配置下面顾问,允许通过引介技术将任何池化对象强转为org.springframework.aop.target.PoolingConfig类型,以获取池的大小等相关配置信息。
51<!--MethodInvokingFactoryBean用于将调用poolTargetSource对象的getPoolingConfigMixin方法创建Bean:poolConfigAdvisor-->2<bean id="poolConfigAdvisor" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.MethodInvokingFactoryBean">3 <property name="targetObject" ref="poolTargetSource"/>4 <property name="targetMethod" value="getPoolingConfigMixin"/>5</bean>通过在AbstractPoolingTargetSource类上调用便捷方法(因此使用MethodInvokingFactoryBean)可获得此顾问程序。该顾问的名称(此处为poolConfigAdvisor)必须位于公开池对象的ProxyFactoryBean中的拦截器名称列表中。如下获取池的最大大小。
31PoolingConfig conf = (PoolingConfig) beanFactory.getBean("businessObject");2System.out.println("Max pool size is " + conf.getMaxSize());3
原型目标源
原型目标源PrototypeTargetSource与池目标源类似,每次方法调用都会创建目标的新实例。
51<bean id="prototypeTargetSource" class="org.springframework.aop.target.PrototypeTargetSource">2 <!--目标Bean(必须为原型Bean)-->3 <property name="targetBeanName" ref="businessObjectTarget"/>4</bean>5
ThreadLocal目标源
如果需要为每个线程创建新的目标对象,则可以使用ThreadLocal目标源。
41<bean id="threadlocalTargetSource" class="org.springframework.aop.target.ThreadLocalTargetSource">2 <property name="targetBeanName" value="businessObjectTarget"/>3</bean>4
4. 切面实例化模型
默认情况下,应用程序上下文中每个切面都有一个实例。 AspectJ 将此称为单例实例化模型。可以使用备用生命周期来定义切面。 Spring 支持 AspectJ 的perthis和pertarget实例化模型(当前不支持percflow, percflowbelow,和pertypewithin)。
您可以通过在@Aspect注解中指定perthis子句来声明perthis切面。
121("perthis(com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService())")2public class MyAspect {3
4 private int someState;5
6 (com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService())7 public void recordServiceUsage() {8 // ...9 }10
11}12
perthis子句的作用是为每个执行业务服务的唯一服务对象(每个与切入点表达式匹配的联接点绑定到“ this”的唯一对象)创建一个切面实例。切面实例是在服务对象上首次调用方法时创建的。当服务对象超出范围时,切面将超出范围。在创建切面实例之前,其中的任何建议都不会执行。创建切面实例后,在其中声明的通知将在匹配的连接点处执行,但仅当服务对象是与此切面相关联的对象时才执行。有关per子句的更多信息,请参见 AspectJ 编程指南。
pertarget实例化模型的工作方式与perthis完全相同,但是它为匹配的连接点处的每个唯一目标对象创建一个方面实例。
注意:使用XML配置方式目前仅支持单例实例化模型,在将来的版本中可能会支持其他实例化模型。
5. Spring与Aspect
请参考Spring官方文档 Core 篇的 5.10 章节Using AspectJ with Spring Applications。
注意:
Spring AOP 默认通过运行期的动态代理来实现AOP的,可额外导入 spring-aspects 依赖来支持通过类加载时编织实现AOP。
6. AOP配置示例
对于一些可重复执行的操作,在执行失败时自动进行重试,该功能涉及多个类的逻辑修改,非常适合使用切面实施。
381public class ConcurrentOperationExecutor implements Ordered {3 private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_RETRIES = 2;4 private int maxRetries = DEFAULT_MAX_RETRIES;5 private int order = 1;6
7 public void setMaxRetries(int maxRetries) {8 this.maxRetries = maxRetries;9 }10
11 public int getOrder() {12 return this.order;13 }14
15 public void setOrder(int order) {16 this.order = order;17 }18
19 ("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService()")20 public Object doConcurrentOperation(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {21 int numAttempts = 0;22 PessimisticLockingFailureException lockFailureException;23 24 do {25 numAttempts++;26 try {27 return pjp.proceed();28 }29 catch(PessimisticLockingFailureException ex) {30 lockFailureException = ex;31 }32 } while(numAttempts <= this.maxRetries);33 34 throw lockFailureException;35 }36
37}38
相应的 Spring 配置如下。请注意,该切面实现了Ordered接口,因此我们可以将切面的优先级设置为高于事务通知,这样就可以在每次重试的时候开启新事务了。
71<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>2
3<bean id="concurrentOperationExecutor" class="com.xyz.myapp.service.impl.ConcurrentOperationExecutor">4 <property name="maxRetries" value="3"/>5 <property name="order" value="100"/>6</bean>7
为了优化切面使用,仅对指定的方法进行重试,我们可以定义一个@Idempotent注解,对需要重试的方法进行标记。
51(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)2public @interface Idempotent {3 // marker annotation4}5
然后,修改切面的切入点表达式,仅对有@Idempotent注解的方法进行匹配,如下所示:
51("com.xyz.myapp.SystemArchitecture.businessService() && @annotation(com.xyz.myapp.service.Idempotent)")2public Object doConcurrentOperation(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {3 ...4}5
如果你更喜欢通过XML进行AOP配置,可参考如下配置示例,配套的Java类去掉AOP相关注解即可。
221<aop:config>2
3 <aop:aspect id="concurrentOperationRetry" ref="concurrentOperationExecutor">4
5 <aop:pointcut id="idempotentOperation"6 expression="execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..)) 7 and @annotation(com.xyz.myapp.service.Idempotent)"/>8
9 <aop:around10 pointcut-ref="idempotentOperation"11 method="doConcurrentOperation"/>12
13 </aop:aspect>14
15</aop:config>16
17<bean id="concurrentOperationExecutor"18 class="com.xyz.myapp.service.impl.ConcurrentOperationExecutor">19 <property name="maxRetries" value="3"/>20 <property name="order" value="100"/>21</bean>22
更多案例请打开SpringAOP-demo工程查看!
demo01:基于XML的事务切面
demo02:基于注解的事务切面
7. SpringAOP相关工具类
Spring读源码系列之AOP--05---aop常用工具类学习大忽悠爱忽悠的博客-CSDN博客aop 工具类](https://blog.csdn.net/m0_53157173/article/details/124361587)
第03章_事务控制
第一节 Spring事务管理简介
Spring为不同类型的事务管理提供了统一的访问接口,使用起来更加简便。
1. Spring事务相关接口
PlatformTransactionManager
Spring事务管理的核心接口为org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager,其声明了事务操作的基本API。
121public interface PlatformTransactionManager {2
3 // 返回当前活动的事务或创建一个新事务,这取决于参数中的事务传播行为4 TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;5
6 // 提交事务(注意:如果事务状态被设置为rollbackOnly,则执行回滚)7 void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;8
9 // 回滚事务10 void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;11}12
TransactionDefinition
事务的相关特性由org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition接口定义。
671public interface TransactionDefinition {2 // 支持当前活动事务,如果不存在活动事务,则创建一个新事务。默认值。3 int PROPAGATION_REQUIRED = 0; 4 5 // 支持当前活动事务,如果不存在事务,则以非事务执行。请谨慎使用!6 int PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS = 1;7 8 // 支持当前活动事务,如果不存在事务,则抛出异常。9 int PROPAGATION_MANDATORY = 2;10 11 // 创建一个新事务,如果存在活动事务,则暂停。12 int PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW = 3;13 14 // 以非事务方式执行,如果存在活动事务,则暂停。15 int PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4;16 17 // 以非事务方式执行,如果存在活动事务,则抛异常。18 int PROPAGATION_NEVER = 5;19 20 // 如果存在活动事务,则创建一个嵌套事务,否则创建一个新事务(注意:并非所有的事务管理器都支持嵌套事务)。21 int PROPAGATION_NESTED = 6;22 23 // 使用数据库的默认隔离级别(MySql默认为可重复读,Oracle默认为读可提交)。24 int ISOLATION_DEFAULT = -1;25 26 // 读未提交27 int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1;28 29 // 读已提交30 int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED = 2;31 32 // 可重复读33 int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4;34 35 // 序列化36 int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE = 8; 37 38 // 使用底层事务系统的默认超时时间,如果不支持则不超时。39 int TIMEOUT_DEFAULT = -1;40
41 default int getPropagationBehavior() {42 return PROPAGATION_REQUIRED;43 }44
45 default int getIsolationLevel() {46 return ISOLATION_DEFAULT;47 }48
49 default int getTimeout() {50 return TIMEOUT_DEFAULT;51 }52
53 default boolean isReadOnly() {54 return false;55 }56
57 58 default String getName() {59 return null;60 }61
62 static TransactionDefinition withDefaults() {63 return StaticTransactionDefinition.INSTANCE;64 }65}66
67
注意:
隔离级别和超时等参数只有在开启新事务时有效,如果是返回当前活动事务,则不会生效。
如果设置了不支持的事务配置选项,则会事务管理器会抛出异常(read-only标志除外)。
关于事务传播行为:
如果当前不存在活动事务时:
创建新事务: 0-PROPAGATION_REQUIRED、3-PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW、6-PROPAGATION_NESTED
非事务执行:1-PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS、4-PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED、5-PROPAGATION_NEVER
抛异常:2-PROPAGATION_MANDATORY
如果当前存在活动事务时:
加入:0-PROPAGATION_REQUIRED、1-PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS、2-PROPAGATION_MANDATORY,要么都提交,要么都回滚(cc-11,rr-00,cr-00,rc-00E,即任一事务回滚,则整个事务都会滚)。
挂起:3-PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW(cc-11,rr-00,cr-10,rc-01)、4-PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED(cc-11,rr-10,cr-10,rc-11),互不干涉。
抛异常:5-PROPAGATION_NEVER,直接抛异常。
创建保存点:6-PROPAGATION_NESTED,可以基于保存点回滚(cc-11,rr-00,cr-00,rc-01)。
TransactionStatus
事务的状态和行为由org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus接口定义。
381
2public interface TransactionStatus extends TransactionExecution, SavepointManager, Flushable {3
4 // 刷新事务(如果事务管理器没有刷新的概念,这个操作可能是无效的)5 void flush();6
7 // 是否存在保存点。可用于实现嵌套事务。8 boolean hasSavepoint();9}10
11
12public interface TransactionExecution {13 // 判断是否为新事务14 boolean isNewTransaction();15
16 // 设置事务为rollback-only状态,表示事务将会进行回滚17 void setRollbackOnly();18
19 // 判断事务是否为rollback-only状态20 boolean isRollbackOnly();21
22 // 判断事务是否已完成(提交或回滚)23 boolean isCompleted();24}25
26
27public interface SavepointManager {28 // 创建保存点29 Object createSavepoint() throws TransactionException;30 31 // 回滚到指定保存点32 void rollbackToSavepoint(Object savepoint) throws TransactionException;33 34 // 显式释放保存点(注意:大部分事务管理器会在事务完成时自动释放保存点)35 void releaseSavepoint(Object savepoint) throws TransactionException;36 37}38
2. PlatformTransactionManager的常用实现
DataSourceTransactionManager
不管是使用声明式事务,还是编程式事务,都必须先注册PlatformTransactionManager的具体实现。如果你使用纯JDBC(或MyBatis),则需要注册DataSourceTransactionManager。DataSourceTransactionManager类是单个JDBC数据源的PlatformTransactionManager实现,它将JDBC连接从指定的数据源绑定到当前正在执行的线程,可能允许每个数据源一个线程连接。
131<!-- 声明一个普通的数据源 -->2<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">3 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />4 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />5 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />6 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />7</bean>8
9<!--注册DataSourceTransactionManager-->10<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">11 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>12</bean>13
HibernateTransactionManager
如果你使用的是 Hibernate 本地事务,则需要注册HibernateTransactionManager。
201<!--定义一个Hibernate的LocalSessionFactoryBean-->2<bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.LocalSessionFactoryBean">3 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>4 <property name="mappingResources">5 <list>6 <value>org/springframework/samples/petclinic/hibernate/petclinic.hbm.xml</value>7 </list>8 </property>9 <property name="hibernateProperties">10 <value>11 hibernate.dialect=${hibernate.dialect}12 </value>13 </property>14</bean>15
16<!--注册HibernateTransactionManager-->17<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager">18 <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"/>19</bean>20
注意:如果DataSource(由任何非JTA事务管理器使用)通过 JNDI 查找并由 Java EE 容器管理,则它应该是非事务性的,因为 Spring 框架(而不是 Java EE 容器)Management 事务。
JtaTransactionManager
如果是在JavaEE容器环境中,通过 JNDI 查找数据源,则一般注册JtaTransactionManager。JtaTransactionManager不需要了解DataSource(或任何其他特定资源),因为它使用了JavaEE容器的全局事务管理基础结构。
181 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"5 xsi:schemaLocation="6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd">10
11 <!-- 从JavaEE容器中查找数据源 -->12 <jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" jndi-name="jdbc/jpetstore"/>13
14 <!--注册JtaTransactionManager-->15 <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager" />16
17</beans>18
提示:如果您使用JTA,则无论使用哪种数据访问技术(无论是JDBC、HibernateJPA或任何其他受支持的技术),事务管理器定义都应该看起来相同。这是由于 JTA 事务是全局事务,它可以征用任何事务资源。
从上面几个案例可以看到,在所有这些情况下,无需更改应用程序代码。您可以仅通过更改配置来更改事务的管理方式,即使更改意味着从本地事务转移到全局事务,反之亦然。
3. 事务管理器与资源同步
上面介绍了如何创建不同的事务管理器,并连接事务所需要的资源(如DataSourceTransactionManager所需的JdbcDataSource等),本节将会介绍在业务代码中如何正确创建、重用和清理这些资源。
首选的方法是使用Spring提供的 JdbcTemplate 等一些高级抽象的解决方案,在其内部处理了资源的创建、重用和清理,以及事务同步和异常处理,使你可以完全专注于业务代码实现。
当然,如果你希望业务代码可以直接访问底层资源,可以通过DataSourceUtils(JDBC)、EntityManagerFactoryUtils(JPA)、SessionFactoryUtils(Hibernate)等类来获取被Spring管理的底层资源实例。
41// 使用DataSourceUtils类代替传统的DataSource获取连接2// 如果当前事务存在连接,则返回该连接,否则创建新的连接,并且供同一事务的后续重用3Connection conn = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);4
第二节 声明式事务管理
Spring声明式事务管理基于SpringAOP实现,可以做到方法级别的精细控制,并且可以自定义回滚规则,设置Rollback-Only状态,以及在事务管理的过程中插入自定义行为等。下面是声明式事务处理的基本流程。
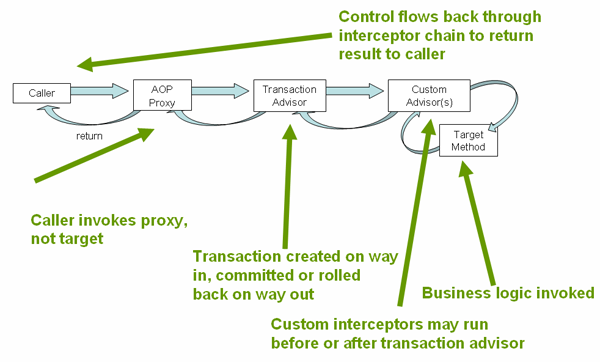
注意:Spring事务不支持跨远程调用传播事务上下文,即事务不能跨远程调用。
1. 声明式事务的基本配置
下面实例,为x.y.service包下的类创建AOP代理,并应用事务通知。
491<!-- from the file 'context.xml' -->2 3<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"6 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"7 xsi:schemaLocation="8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">14
15 <!-- 业务Bean -->16 <bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/>17
18 <!-- 事务通知配置。使用txManager事务管理器(如果其名称包含transactionManager,则可省略) -->19 <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">20 <tx:attributes>21 <!-- get开头的方法以只读事务执行 -->22 <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>23 <!-- 其它方法以默认的事务配置执行 -->24 <tx:method name="*"/>25 </tx:attributes>26 </tx:advice>27
28 <!-- 将事务通知配置为顾问(提示:顾问是只有一个通知的切面) -->29 <aop:config>30 <aop:pointcut id="serviceOperation" expression="execution(* x.y.service.*.*(..))"/>31 <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="serviceOperation"/>32 </aop:config>33
34 <!-- 事务管理器 -->35 <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">36 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>37 </bean>38
39 <!-- 事务管理器依赖的数据源 -->40 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">41 <property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/>42 <property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@rj-t42:1521:elvis"/>43 <property name="username" value="scott"/>44 <property name="password" value="tiger"/>45 </bean>46 47</beans>48
49
下面是一个测试代码。
131public final class Boot {2
3 public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {4 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("context.xml", Boot.class);5 6 // 从容器获取被代理的服务Bean7 FooService fooService = (FooService) ctx.getBean("fooService");8 9 // 执行业务方法,并进行事务控制10 fooService.insertFoo (new Foo());11 }12}13
2. 配置多个事务通知
你可以为不同的Bean配置不同的事务通知。
421 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"5 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"6 xsi:schemaLocation="7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">13
14 <aop:config>15 <!-- 为service包下以 Service 结尾的类配置默认的事务通知:defaultTxAdvice-->16 <aop:pointcut id="defaultServiceOperation" expression="execution(* x.y.service.*Service.*(..))"/>17 <aop:advisor pointcut-ref="defaultServiceOperation" advice-ref="defaultTxAdvice"/>18
19 <!-- 为service包下以 Manager 结尾的类配置另外的事务通知:noTxAdvice-->20 <aop:pointcut id="noTxServiceOperation" expression="execution(* x.y.service.*Manager.*(..))"/>21 <aop:advisor pointcut-ref="noTxServiceOperation" advice-ref="noTxAdvice"/>22 </aop:config>23
24 <!-- 配置事务通知 defaultTxAdvice(由于事务管理器的名称为transactionManager,因此transaction-manager属性被省略) -->25 <tx:advice id="defaultTxAdvice">26 <tx:attributes>27 <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>28 <tx:method name="*"/>29 </tx:attributes>30 </tx:advice>31
32 <!-- 配置事务通知noTxAdvice(由于事务管理器的名称为transactionManager,因此transaction-manager属性被省略) -->33 <tx:advice id="noTxAdvice">34 <tx:attributes>35 <tx:method name="*" propagation="NEVER"/>36 </tx:attributes>37 </tx:advice>38
39 <!-- 事务管理器、数据源和业务Bean相关配置已省略 -->40
41</beans>42
3. 事务通知配置详解
下表是事务通知的一些属性和配置含义。
| 属性名 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| name | 方法名称。可用*表示任意字符。 | |
| propagation | 事务传播行为。详情参考上一章节内容。 | REQUIRED |
| isolation | 事务隔离级别。仅适用于REQUIRED或REQUIRES_NEW的传播设置。 | DEFAULT |
| timeout | 事务超时(秒)。仅适用于传播REQUIRED或REQUIRES_NEW。 | -1 |
| read-only | 读写与只读事务。仅适用于REQUIRED或REQUIRES_NEW | false |
| rollback-for | 触发回滚的异常列表,以逗号分隔。 | |
| no-rollback-for | 不触发回滚的异常列表,以逗号分隔。 |
下面是事务回滚异常列表配置示例。默认情况下,如果出现运行时异常(RuntimeException)或错误(Error),则回滚事务,否则提交事务。你可以通过设置回滚规则(rollback-for)或不回滚规则(no-rollback-for)来修改需要回滚事务的异常。
71<tx:advice id="txAdvice">2 <tx:attributes>3 <!--除InstrumentNotFoundException之外的任何异常都会导致事务的回滚-->4 <tx:method name="*" rollback-for="Throwable" no-rollback-for="InstrumentNotFoundException"/>5 </tx:attributes>6</tx:advice>7
你也可以使用编程式事务控制来实现上述控制,但这会使你的代码与Spring框架耦合,尽量不要使用它。
121public void resolvePosition() {2try {3// 业务代码4} catch (InstrumentNotFoundException infe) {5// 不回滚6} catch (Throwable t) {7// 回滚8TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();9}10}12
4. 声明式事务的注解配置方式
除了使用XML进行声明式事务配置外,还可以使用Spring提供的注解方式进行配置,主要用到的注解为@EnableTransactionManagement和@Transactional。
开启事务注解配置支持
首先,在配置类上加@EnableTransactionManagement注解,开启注解事务支持。
51public class SpringConfig {4}5
下面表格是@EnableTransactionManagement注解的一些属性配置。
| 注解属性 | XML属性 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 不适用 | transaction-manager | 要使用的事务管理器bean名称 | transactionManager |
| mode | mode | 默认的proxy-表示使用SpringAOP代理。aspectj-表示使用AspectJ编织,这需要spring-aspects.jar包,并启用加载时编织或编译时编织。 | proxy |
| proxyTargetClass | proxy-target-class | 是否使用CGLib创建基于子类的动态代理,仅适用于proxy模式。 | false |
| order | order | 事务通知的应用顺序,一般为最低优先级(值越大优先级越低)。 | Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE |
等效的XML配置如下:
61<!--开启注解事务支持-->2<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>3
4<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">5 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>6</bean>
在类或方法上开启事务
在类或方法上加@Transactional注解,Spring在创建相关Bean时,会自动进行AOP代理,应用事务通知。
101 // 1. @Transactional注解加载类上,表示该类的所有public方法都支持事务2public class DefaultFooService implements FooService {3
4 Foo getFoo(String fooName);5
6 // 2. @Transactional注解也可以加在方法上,进行单独的控制7 void updateFoo(Foo foo);8}9
10
下面表格是@Transactional 注解的一些属性配置。
| 属性名 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| value | 要使用的事务管理器bean名称或限定符值 | transactionManager |
| propagation | 事务传播行为 | PROPAGATION_REQUIRED |
| isolation | 事务隔离级别 | ISOLATION_DEFAULT |
| timeout | 事务超时时间。-1表示基础事务系统的默认超时时间或无超时 | -1 |
| readOnly | 事务是否只读 | false |
| rollbackFor/rollbackForClassName | 触发回滚的异常列表(Class/String类型),以逗号分隔。 | |
| noRollbackFor/noRollbackForClassName | 不触发回滚的异常列表(Class/String类型),以逗号分隔。 |
注意:显示在事务监视器(例如,WebLogic 的事务监视器)和日志输出中的事务名称暂时无法指定,但它一般是
全类名.方法名,例如,BusinessService类的handlePayment(..)方法启动了事务,则事务的名称应为com.example.BusinessService.handlePayment。
下面是使用@Transactional注解的几点注意事项:
@Transactional注解只会对public方法生效,protected和private方法上的该注解将会被忽略。
不建议将@Transactional注解加在接口上,因为它只适用于基于接口的AOP代理,而在创建基于子类的AOP代理时无效。
也不建议将@Transactional注解加在父类上,因为子类不会继承该注解。
只有通过代理对象调用public方法才会进行事务控制,通过this(实际对象)的自调用无法执行事务通知,不进行事务控制。
你不能在未完全初始化时依赖Spring提供的事务控制,比如在@PostConstruct标注的方法中,这时可能尚未应用事务通知。
选择不同的事务管理器
一般情况下,Spring应用程序使用一个事务管理器就够了,但某些特殊情形,你可能需要多个独立的事务管理器。这时,可以通过@Transactional注解的value属性来指定所需要的事务管理器bean名称或指定一个匹配限定符。
如下案例演示了如何使用限定符来选择不同的事务管理器。首先,先配置两个不同的事务管理器。
81<!--配置一个事务管理器1,指定限定符为order-->2<bean id="transactionManager1" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">3 <qualifier value="order"/>4</bean>5<!--配置一个事务管理器2,指定限定符为account-->6<bean id="transactionManager2" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">7 <qualifier value="account"/>8</bean>然后,在代码中通过限定符来进行匹配。
101public class TransactionalService {2
3 // 匹配事务管理器14 ("order")5 public void setSomething(String name) { ... }6
7 // 事务管理器28 ("account")9 public void doSomething() { ... }10}提示:如果限定符匹配不到事务管理器,则会选用默认的事务管理器transactionManager。
利用组合注解简化事务配置
如果发现您在许多不同的方法上重复使用@Transactional的相同属性,则可将其定义为自定义的组合注解,简化配置。
141// 使用OrderTx注解替代@Transactional(value="order", propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)等一串配置2({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})3(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)4(value="order", propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)5public @interface OrderTx {6}7
8// 使用OrderTx注解替代@Transactional("account")等一串配置9({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})10(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)11("account")12public @interface AccountTx {13}14
自定义注解定义好后,就可以在代码中使用了。
91public class TransactionalService {2
3 4 public void setSomething(String name) { ... }5
6 7 public void doSomething() { ... }8}9
第三节 编程式事务管理
Spring提供了两种编程式事务管理的方式,分别是使用TransactionTemplate和直接执行 PlatformTransactionManager。
1. TransactionTemplate
TransactionTemplate与JdbcTemplate等模板的设计类似,采用回调的方式传入业务代码。
执行事务方法
如果执行的方法带有返回值,执行时传入TransactionCallback接口的实例。
231public class SimpleService implements Service {2 // 事务模板3 private final TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;4
5 // 使用构造器注入 PlatformTransactionManager6 public SimpleService(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {7 8 // 初始化事务模板9 this.transactionTemplate = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);10 }11
12 public Object someServiceMethod() {13 14 // 执行事务操作,并返回执行结果15 return transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallback() {16 public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {17 updateOperation1();18 return resultOfUpdateOperation2();19 }20 });21 }22}23
如果执行的方法不带返回值,执行时传入TransactionCallbackWithoutResult接口的实例。
71transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {2 protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status) {3 updateOperation1();4 updateOperation2();5 }6});7
如果需要进行回滚,可以调用TransactionStatus对象上的setRollbackOnly()方法来回滚事务,如下所示:
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
81protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status) {2try {3updateOperation1();4updateOperation2();5} catch (SomeBusinessException ex) {6status.setRollbackOnly();7}8}
});
修改事务配置
可以调用TransactionTemplate的相关方法修改事务配置,例如传播模式,隔离级别,超时等。
141public class SimpleService implements Service {2 // 事务模板3 private final TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;4
5 public SimpleService(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {6 // 初始化事务模板7 this.transactionTemplate = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);8
9 // 修改默认的事务配置10 this.transactionTemplate.setIsolationLevel(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED);11 this.transactionTemplate.setTimeout(30); 12 }13}14
定义共享的事务模板实例
以下示例通过使用 Spring XML 配置来定义具有一些自定义事务设置的TransactionTemplate。
51<bean id="sharedTransactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">2 <property name="isolationLevelName" value="ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED"/>3 <property name="timeout" value="30"/>4</bean>5
然后,您可以根据需要将sharedTransactionTemplate注入到尽可能多的服务中。
注意:
TransactionTemplate类的实例是线程安全的,因为该实例不维护任何对话状态。
但TransactionTemplate实例会维持配置状态,因此尽管许多类可以共享一个TransactionTemplate的单个实例,但是如果一个类需要使用具有不同设置(例如,不同的隔离级别)的TransactionTemplate,则需要创建两个不同的TransactionTemplate实例。
2. PlatformTransactionManager
您也可以直接使用org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager来管理您的事务。以下示例显示了如何执行此操作:
271// 注入事务管理器2private PlatformTransactionManager txManager;4
5/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////6
7// 创建一个默认的事务配置8DefaultTransactionDefinition transactionDefinition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();9// 设置事务名称(注:事务名称仅能通过编程式进行设置)10transactionDefinition.setName("SomeTxName");11// 设置事务隔离级别12transactionDefinition.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED);13
14// 获取当前活动事务或创建新事务15TransactionStatus status = txManager.getTransaction(transactionDefinition);16try {17 // 业务代码18}19catch (MyException ex) {20 // 回滚事务21 txManager.rollback(status);22 throw ex;23}24
25// 提交事务26txManager.commit(status);27
第四节 其它
1. 事务绑定事件
如果你希望发布的事件在事件源事务的特定阶段触发(一般是事务提交后触发),则可以使用@TransactionalEventListener来替代原有的@EventListener注解。如下示例:
91public class MyComponent {3
4 5 public void handleOrderCreatedEvent(CreationEvent<Order> creationEvent) {6 ...7 }8}9
特别的,可以使用其 phase 属性指定触发时机,可选的值有BEFORE_COMMIT,AFTER_COMMIT(默认),AFTER_ROLLBACK和AFTER_COMPLETION。
如果不存在事务,默认不调用侦听器,但你也可以设置 fallbackExecution 属性设置为true来覆盖该行为。
2. 在 AspectJ 中使用@Transactional
3. 与特定服务器的集成
第04章_ORM框架
Spring框架对JDBC进行了封装和抽象,隐藏了许多样板化的使用细节,提供了多种更加方便的操作方式,如JdbcTemplate和NamedParameterJdbcTemplate、SimpleJdbcInsert和SimpleJdbcCall以及MappingSqlQuery、SqlUpdate和StoredProcedure等。除此之外,还将JDBC的SqlException异常(甚至Hibernate或JPA等框架特有的异常)转换为自己的异常层次结构(DataAccessException),使您可以轻松地在上述持久性技术之间进行切换。
下面列表展示了使用JDBC查询数据库时Spring为你做了哪些事项:
| Action | Who? |
|---|---|
| 1. 定义连接参数 | ✓ |
| 2. 打开连接 | ✕ |
| 3. 指定 SQL 语句 | ✕ |
| 4. 声明参数并提供参数值 | ✓ |
| 5. 准备并执行该语句 | ✓ |
| 6. 设置循环以遍历结果(如果有) | ✕ |
| 7. 进行每次迭代的工作 | ✓ |
| 8. 处理任何异常 | ✕ |
| 9. 处理事务 | ✕ |
| 10. 关闭连接,语句和结果集 | ✕ |
提示:确保您的数据访问对象(DAO)或存储库进行异常转换的最佳方法是使用
@Repository注解。
第一节 JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate是Spring提供的操作数据库最基本的方式。它负责处理资源的创建和释放(如打开和关闭连接)以及JDBC工作流程的基本任务(如PS的创建和执行)等,只需应用程序提供SQL和对执行结果进行处理即可。
1. 配置Jdbctemplate
1.1 XML方式配置
常见的做法是配置所需的数据源为Bean,并将其注入到Dao类中,然后在数据源的set方法中创建JdbcTemplate。
121public class UserDao {2 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;3
4 // 数据源的set方法,用于属性注入5 public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {6 // 在set方法中创建JdbcTemplate7 this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);8 }9 10 // ...11}12
与之配套的XML配置如下:
271 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"5 xsi:schemaLocation="6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">10
11 <context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>12
13 <!--配置数据源为bean-->14 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">15 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>16 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>17 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>18 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>19 </bean>20
21 <!--配置Dao类为bean,并注入数据源-->22 <bean id="userDao" class="com.example.UserDao">23 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>24 </bean>25
26</beans>27
除此之外,也可直接在XML中配置一个默认的JdbcTemplate,直接注入JdbcTemplate到Dao类中。
41<bean id="defaultJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">2 <constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />3</bean>4
简单起见,在实际项目过程中,可以使Dao类继承JdbcDaoSupport类,则会继承来自其的setDataSource(..)方法和setJdbcTemplate(...)方法,使用Dao类时直接注入其中任意一个即可。
注意:JdbcTemplate与Spring的其它模板类相似,其会话数据是线程安全的,但是配置信息(如数据库连接信息)是线程不安全的。
1.2 注解方式配置
Spring也支持使用注解方式配置JdbcTemplate,一般采用@Repository注解将Dao配置为Bean,然后使用@Autowired注解注入数据源。
121 2public class UserDao{3 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;4
5 6 public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {7 this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);8 }9
10 // ...11}12
与之配套的XML配置如下:
241 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"5 xsi:schemaLocation="6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">10
11 <context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>12 13 <!-- 组件扫描 -->14 <context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.docs.test" />15
16 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">17 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>18 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>19 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>20 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>21 </bean>22
23</beans>24
2. 使用JdbcTemplate
2.1 查询单行记录
queryForObject
201public String findNameById() {3 return getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject("select username from user where id = ?", String.class, 1);4}5
6public User findById() {8 return getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject("select * from user where id = ?", new RowMapper<User>() {9 10 public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {11 User user = new User();12 user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));13 user.setUserName(rs.getString("username"));14 user.setBirthDay(rs.getTimestamp("birthday"));15 user.setSex(rs.getString("sex"));16 user.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));17 return user;18 }19 }, 1);20}关于RowMapper:
它提供一个回调函数
mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum),用于告诉JdbcTemplate如何从结果集拿数据并封装到VO对象。特别的,如果列名和字段名一致,可以使用new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class)来简化,下面将会使用到该种方式。
queryForMap
41public Map<String, Object> findById2() {3 return getJdbcTemplate().queryForMap("select * from user where id = ?", 1);4}
2.2 查询多行记录
query
41public List<User> findAll() {3 return getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from user", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));4}
queryForList
51public List<Map<String, Object>> findAll2() {3 return getJdbcTemplate().queryForList("select * from user");4}5
2.3 查询返回结果集
queryForRowSet
41public SqlRowSet findAll3() {3 return getJdbcTemplate().queryForRowSet("select * from user");4}
2.4 执行更新语句
普通更新语句
61public int insert(User user) {3 return getJdbcTemplate().update("insert into user (id, username, birthday, sex, address) values(NULL,?,?,?,?)",4 user.getUserName(), user.getBirthDay(), user.getSex(), user.getAddress());5}6
提示:在JDBC中,insert、update和delete语句都视为更新语句,处理逻辑一致!
返回自增列值的插入语句
201public int insert2(User user) {3 KeyHolder keyHolder = new GeneratedKeyHolder();4 int update = getJdbcTemplate().update(5 new PreparedStatementCreator() {6 7 public PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException {8 PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement("insert into user (id, username, birthday, sex, address) values(NULL,?,?,?,?)", new String[]{"id"});9 ps.setString(1, user.getUserName());10 ps.setTimestamp(2, user.getBirthDay());11 ps.setString(3, user.getSex());12 ps.setString(4, user.getAddress());13 return ps;14 }15 },16 keyHolder);17
18 return update > 0 ? keyHolder.getKey().intValue() : update;19}20
注意:
插入时检索自增列值需要驱动支持JDBC3.0标准。
需要自定义PreparedStatement,在第二个字段指定自增列名。
一次执行多条更新语句
21// 一次传入多条无参数的SQL语句2int[] batchUpdate(final String... sql)
2.5 执行DDL语句
excute
81public int createBackupTable() {3 getJdbcTemplate().execute("drop table if exists user_bak");4
5 getJdbcTemplate().execute("create table user_bak like user");6 return 0;7}8
2.6 批量更新
自动设置PS(List<BasicObject[]>)
51// 占位符形式的SQL语句,通过List<Object[]>传入参数2int[] batchUpdate(String sql, List<Object[]> batchArgs)3
4// 占位符形式的SQL语句,通过List<Object[]>传入参数,并显式指定参数类型5int[] batchUpdate(String sql, List<Object[]> batchArgs, final int[] argTypes)181public class JdbcActorDao implements ActorDao {3 4 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;5
6 public int[] batchUpdate(final List<Actor> actors) {7 List<Object[]> batch = new ArrayList<Object[]>();8 9 for (Actor actor : actors) {10 Object[] values = new Object[]{actor.getFirstName(), actor.getLastName(), actor.getId()};11 batch.add(values);12 }13 14 return this.jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("update t_actor set first_name = ?, last_name = ? where id = ?", batch);15 }16
17}18
注意:必须保证Object数组中对象的顺序和设置参数时的顺序一致!
手动设置PS(List<BizObject>)
21// 占位符形式的SQL语句,通过BatchPreparedStatementSetter接口设置PS(需通过匿名内部类隐式传入一个对象列表)2int[] batchUpdate(String sql, final BatchPreparedStatementSetter pss)231public class JdbcActorDao implements ActorDao {3 4 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;5
6 public int[] batchUpdate(final List<Actor> actors) {7 8 return this.jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate( "update t_actor set first_name = ?, last_name = ? where id = ?",9 new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {10 // 设置PS(actors为隐式传入的对象列表)11 public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException {12 ps.setString(1, actors.get(i).getFirstName());13 ps.setString(2, actors.get(i).getLastName());14 ps.setLong(3, actors.get(i).getId().longValue());15 }16 17 // setValues的执行次数18 public int getBatchSize() {19 return actors.size();20 }21 });22 }23}注意:如果流或从文件中读取,可能最后一批可能没有该数量的条目。在这种情况下,您可以使用
InterruptibleBatchPreparedStatementSetter接口,在合适的时候调用isBatchExhausted方法中断批处理。
2.7 分批次批量更新
21// 占位符形式的SQL语句,通过Collection<T>传入参数,通过ParameterizedPreparedStatementSetter接口设置PS,支持分批次更新2int[][] batchUpdate(String sql, final Collection<T> batchArgs, final int batchSize, final ParameterizedPreparedStatementSetter<T> pss)201public class JdbcActorDao implements ActorDao {3 4 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;5
6 public int[][] batchUpdate(final Collection<Actor> actors) {7 int[][] updateCounts = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(8 "update t_actor set first_name = ?, last_name = ? where id = ?",9 actors,10 100,11 new ParameterizedPreparedStatementSetter<Actor>() {12 public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, Actor argument) throws SQLException {13 ps.setString(1, argument.getFirstName());14 ps.setString(2, argument.getLastName());15 ps.setLong(3, argument.getId().longValue());16 }17 });18 return updateCounts;19 }20}该方法返回值为一个二维数组,外层数组长度表示已执行的批次数,内层数组的长度表示每批处理的数量,元素的值表示一次更新语句的返回值。如果JDBC程序不支持,则为-2。
3. NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate舍弃传统占位符(?)的方式,使用更语义化的变量名称来占位。其参数通过Map或SqlParameterSource的形式传入。SqlParameterSource有三个实现类,分别为MapSqlParameterSource、BeanPropertySqlParameterSource和EmptySqlParameterSource,下面将会介绍它们的使用。
3.1 Map<String,Object>类型参数
141private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;2public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {3 this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate = new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(dataSource);4}5
6public int countOfActorsByFirstName(String firstName) {7 // 名称占位符形式的SQL语句8 String sql = "select count(*) from T_ACTOR where first_name = :first_name";9 // 准备参数(Map<String,Object>形式)10 Map<String, String> namedParameters = Collections.singletonMap("first_name", firstName);11 // 执行12 return this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, namedParameters, Integer.class);13}14
3.2 MapSqlParameterSource类型参数
81public int countOfActorsByFirstName(String firstName) {2 String sql = "select count(*) from T_ACTOR where first_name = :first_name";3 // 准备参数(MapSqlParameterSource形式)4 SqlParameterSource namedParameters = new MapSqlParameterSource();5 namedParameters.addValue("first_name", firstName);6 return this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, namedParameters, Integer.class);7}8
3.3 BeanPropertySqlParameterSource类型参数
71public int countOfActors(Actor exampleActor) {2 String sql = "select count(*) from T_ACTOR where first_name = :firstName and last_name = :lastName";3 // 准备参数(BeanPropertySqlParameterSource),注意属性名和命名参数一致4 SqlParameterSource namedParameters = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(exampleActor);5 return this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, namedParameters, Integer.class);6}7
提示:
除了上述两个实现类,SqlParameterSource还有一个空实现
EmptySqlParameterSource,常用来占位使用。NamedParameterJdbcTemplate是对JdbcTemplate的封装,如果需要访问包装的JdbcTemplate实例以访问仅在JdbcTemplate类中提供的功能,可以使用getJdbcOperations()方法获取
3.4 批量更新
使用Map数组批量更新
11int[] batchUpdate(String sql, Map<String, ?>[] batchValues)
使用SqlParameterSource数组批量更新
11int[] batchUpdate(String sql, SqlParameterSource[] batchArgs)151public class JdbcActorDao implements ActorDao {2 private NamedParameterTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;3 4 public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {5 this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate = new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(dataSource);6 }7
8 public int[] batchUpdate(List<Actor> actors) {9 return this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(10 "update t_actor set first_name = :firstName, last_name = :lastName where id = :id",11 SqlParameterSourceUtils.createBatch(actors));12 }13
14}15
提示:
SqlParameterSourceUtils.createBatch可你帮助你将List<BizObject>转换为SqlParameterSource[]类型!
4. SQLExceptionTranslator
SQLExceptionTranslator用于将数据库异常转换为Spring中定义的DataAccessException异常。根据不同的转换策略,定义了三个实现类,分别是SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator、SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator和SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator。
4.1 异常转换流程
默认情况下,使用SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator进行数据库异常的转换,它通过SQLErrorCodesFactory加载类路径下的名为sql-error-codes.xml的文件,并通过数据库元数据中的DatabaseProductName查找匹配的SQLErrorCodes用于异常转换。该文件位于org.springframework.jdbc.support包下,配置示例如下。
311 2<beans>4 <bean id="MySQL" class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes">5 <property name="databaseProductNames">6 <list>7 <value>MySQL</value>8 <value>MariaDB</value>9 </list>10 </property>11 <property name="badSqlGrammarCodes">12 <value>1054,1064,1146</value>13 </property>14 <property name="duplicateKeyCodes">15 <value>1062</value>16 </property>17 <property name="dataIntegrityViolationCodes">18 <value>630,839,840,893,1169,1215,1216,1217,1364,1451,1452,1557</value>19 </property>20 <property name="dataAccessResourceFailureCodes">21 <value>1</value>22 </property>23 <property name="cannotAcquireLockCodes">24 <value>1205,3572</value>25 </property>26 <property name="deadlockLoserCodes">27 <value>1213</value>28 </property>29 </bean>30</beans>31
提示:该文件可以被类路径根目录下同名文件覆盖!
如果使用SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator不能转换数据库异常,则采用后备转换器SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator,如果仍不能转换,再使用SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator。
4.2 扩展异常转换器
你可以对SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator进行扩展,如下示例,将特定的错误代码(-12345)转换为DeadlockLoserDataAccessException异常,而其他错误则仍由默认转换器实现转换。
101public class CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslator extends SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator {2
3 protected DataAccessException customTranslate(String task, String sql, SQLException sqlex) {4 if (sqlex.getErrorCode() == -12345) {5 return new DeadlockLoserDataAccessException(task, sqlex);6 }7 return null;8 }9}10
若要使此转换器生效,必须通过setExceptionTranslator方法将其传递给JdbcTemplate。
171private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;2
3public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {4 this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();5 this.jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);6
7 // 创建一个自定义异常转换器,设置给JdbcTemplate8 CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslator tr = new CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslator();9 tr.setDataSource(dataSource);10 this.jdbcTemplate.setExceptionTranslator(tr);11
12}13
14public void updateShippingCharge(long orderId, long pct) {15 this.jdbcTemplate.update("update orders set shipping_charge = shipping_charge * ? / 100 where id = ?", pct, orderId);16}17
注意:在创建CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslator时需要传递一个数据源,以获取数据库元数据查找sql-error-codes.xml对应配置信息。
第二节 其它补充
1. 高级抽象的数据访问方式
1.1 SimpleJdbc
SimpleJdbcInsert和SimpleJdbcCall通过JDBC驱动程序提供数据库元数据来简化用户配置。下面是一些简单示例,具体介绍可参考文档。
221public class JdbcActorDao implements ActorDao {2 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;3 private SimpleJdbcInsert insertActor;4
5 public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {6 this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);7 this.insertActor = new SimpleJdbcInsert(dataSource)8 // 指定插入的表名9 .withTableName("t_actor")10 // 指定自增列11 .usingGeneratedKeyColumns("id");12 }13
14 public void add(Actor actor) {15 // 转换参数16 SqlParameterSource parameters = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(actor);17 // 执行并返回生成的key18 Number newId = insertActor.executeAndReturnKey(parameters);19 actor.setId(newId.longValue());20 }21}22
1.2 JdbcObject
org.springframework.jdbc.object包包含一些类,这些类使您可以以更加面向对象的方式访问数据库,具体介绍请参考官方文档。
2. 特殊参数和值的处理
2.1 提供参数的JDBC类型
一般来说,Spring可以根据传入参数的Java类型来推断JDBC类型。但如果参数值为null时,可能无法识别Java类型,则需要调用ParameterMetaData.getParameterType来获取JDBC类型,这对JDBC驱动程序来说可能很昂贵。你可以升级最新的驱动程序版本,并将spring.jdbc.getParameterType.ignore属性设置为true来禁用此功能,并且通过下面一些方式对可能为null的参数显式传入JDBC类型。
使用
int[] argTypes类型的附加参数。其值为java.sql.Types枚举,JdbcTemplate中许多方式都支持该种方式。使用
SqlParameterValue类包装需要此附加信息的参数值。使用
void registerSqlType(String paramName, int sqlType)方法为参数名注册JDBC类型。但是它仅支持使用SqlParameterSource作为参数的方法。使用BatchPreparedStatementSetter手动设置PS等。
2.2 传入IN子句的值列表
对如类似select * from T_ACTOR where id in (1, 2, 3)的SQL语句,由于JDBC驱动不支持可变数量的占位符,因此对于IN子句的参数列表设置需要动态拼接字符串来实现。在Spring中,可以使用NamedParameterJdbcTemplate来让Spring帮你完成该拼接过程,你只需要传入一个参数值列表即可。
121 2 public List<User> findByIds(List<Integer> ids) {3 // 创建使用命名参数占位符的模板4 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate = new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(getJdbcTemplate());5
6 // 准备参数7 MapSqlParameterSource mapSqlParameterSource = new MapSqlParameterSource();8 mapSqlParameterSource.addValue("ids", ids);9 10 return namedParameterJdbcTemplate.query("select * from user where id in (:ids)", mapSqlParameterSource, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));11 }12 特别的,如果你的数据库支持类似select * from T_ACTOR where (id, last_name) in ((1, 'Johnson'), (2, 'Harrop'))的语法,你可以传入一个对象列表,Spring会自动进行处理。
注意:一般数据库对IN中的条目数有限制,列如Oracle限制为1000。
2.3 处理BLOB和CLOB对象
JdbcTemplate支持BLOB(二进制大对象)和CLOB(字符型大对象)类型的参数值和查询结果处理。详情查看官方文档。
2.4 对存储过程和函数的支持
可以通过SimpleJdbcCall和StoredProcedure来操作存储过程或函数,还支持使用特定于数据库的复杂类型。详情查看官方文档。
3. 嵌入式数据库支持
嵌入式数据库由于其轻量级的特性,易于配置并且启动时间短,在开发和测试的过程中非常有用。Spring在org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.embedded包提供对嵌入式数据库引擎的支持,内置了HSQL、H2和Derby三种嵌入式数据库。此外,你也可以使用扩展API来支持新的嵌入式数据库类型。
3.1 创建嵌入式数据库
XML方式
61<!--创建一个嵌入式数据库,名称为dataSource-->2<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" generate-name="true">3 <jdbc:script location="classpath:schema.sql"/>4 <jdbc:script location="classpath:test-data.sql"/>5</jdbc:embedded-database>6
提示:
默认的数据库类型为EmbeddedDatabaseType.HSQL,你可以通过
type属性修改为H2或DERBY。请将generate-name属性设置为true,生成唯一名称,否则在创建嵌入式数据库时会被连接到同名的数据库实例上。
Java配置方式
161public class DataSourceConfig {3
4 5 public DataSource dataSource() {6 return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()7 .generateUniqueName(true)8 .setType(H2)9 .setScriptEncoding("UTF-8")10 .ignoreFailedDrops(true)11 .addScript("schema.sql")12 .addScripts("user_data.sql", "country_data.sql")13 .build();14 }15}16
Java代码方式
131// 启动数据库2EmbeddedDatabase db = new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()3 .generateUniqueName(true)4 .setType(H2)5 .setScriptEncoding("UTF-8")6 .ignoreFailedDrops(true)7 .addScript("schema.sql")8 .addScripts("user_data.sql", "country_data.sql")9 .build();10 11// 关闭数据库12db.shutdown()13
3.2 使用嵌入式数据库
嵌入式数据库的使用和其它JDBC数据源的使用方式类似。
251public class DataAccessIntegrationTestTemplate {2 private EmbeddedDatabase db;3
4 5 public void setUp() {6 // 使用默认脚本(classpath:schema.sql and classpath:data.sql)创建一个HSQL数据库7 db = new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()8 .generateUniqueName(true)9 .addDefaultScripts()10 .build();11 }12
13 14 public void testDataAccess() {15 JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(db);16 template.query( /* ... */ );17 }18
19 20 public void tearDown() {21 // 关闭数据库22 db.shutdown();23 }24}25
提示:如果你在多个测试类中使用,应该将它注册到Spring容器中管理。
3.3 扩展嵌入式数据库
您可以通过两种方式扩展 Spring JDBC 嵌入式数据库的支持:
实现
EmbeddedDatabaseConfigurer以支持新的嵌入式数据库类型。实施
DataSourceFactory以支持新的DataSource实施,例如用于管理嵌入式数据库连接的连接池。
4. 关于数据源
数据源(DataSource)是JDBC规范的一部分,是通用的连接工厂,Spring通过数据源获得与数据库的连接。你可以从JNDI查找数据源,也可以使用第三方提供的连接池实现来配置自己的数据源。
4.1 创建数据源
DriverManagerDataSource
91<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>2
3<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">4 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>5 <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>6 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>7 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>8</bean>9 等效的代码如下:
61DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();2dataSource.setDriverClassName("org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver");3dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:hsqldb:hsql://localhost:");4dataSource.setUsername("sa");5dataSource.setPassword("");6 注意:
DriverManagerDataSource是一个Spring内置的数据源,每次获取时都返回新连接,不对连接进行缓存,仅用于测试目的。与此类似的还有其实现类
SingleConnectionDataSource。更多关于Spring对
javax.sql.DataSource的实现可以查看SmartDataSource接口和AbstractDataSource抽象类。
DBCP DataSource
171<bean id="dataSource3" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> 2 <!-- 注入连接属性 --> 3 <property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}"></property> 4 <property name="url" value="${url}"></property> 5 <property name="username" value="${username}"></property> 6 <property name="password" value="${password}"></property> 7 8 <!-- 设置初始化连接池大小 --> 9 <property name="initialSize" value="5"></property> 10 <!-- 设置最大连接数 --> 11 <property name="maxIdle" value="50"></property> 12 <!-- 设置最大活动连接数 --> 13 <property name="maxActive" value="10"></property> 14 <!-- 设置等待时间 --> 15 <property name="maxWait" value="5000"></property> 16</bean>17
C3P0 DataSource
151<bean id="dataSource2" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close">2 <!-- 注入连接属性 -->3 <property name="driverClass" value="${driverClassName}"></property>4 <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${url}"></property>5 <property name="user" value="${username}"></property>6 <property name="password" value="${password}"></property>7 8 <!-- 设置初始化连接池大小 -->9 <property name="initialPoolSize" value="5"></property>10 <!-- 设置最大连接数 -->11 <property name="maxPoolSize" value="50"></property>12 <!-- 设置最小的连接数 -->13 <property name="minPoolSize" value="10"></property>14</bean>15
Druid DataSource
181<bean id="dataSource2" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init">2 <!-- 注入连接属性 -->3 <property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}"></property>4 <property name="url" value="${url}"></property>5 <property name="username" value="${username}"></property>6 <property name="password" value="${password}"></property>7 8 <!-- 设置初始化连接池大小 -->9 <property name="initialSize" value="5"></property>10 <!-- 最大连接数 -->11 <property name="maxActive" value="10"></property>12 <!-- 设置等待时间 -->13 <property name="maxWait" value="5000"></property>14 <!-- -->15 <property name="filters" value="stat"></property>16
17</bean>18
Hikari DataSource
211<bean id="dataSourceHikari" class="com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource"2 destroy-method="shutdown">3 <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />4 <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />5 <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />6 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />7 8 <!-- 连接只读数据库时配置为true, 保证安全 -->9 <property name="readOnly" value="false" />10 <!-- 等待连接池分配连接的最大时长(毫秒),超过这个时长还没可用的连接则发生SQLException, 缺省:30秒 -->11 <property name="connectionTimeout" value="30000" />12 <!-- 一个连接idle状态的最大时长(毫秒),超时则被释放(retired),缺省:10分钟 -->13 <property name="idleTimeout" value="600000" />14 <!-- 一个连接的生命时长(毫秒),超时而且没被使用则被释放(retired),缺省:30分钟,建议设置比数据库超时时长少30秒,参考MySQL 15 wait_timeout参数(show variables like '%timeout%';) -->16 <property name="maxLifetime" value="1800000" />17 <!-- 连接池中允许的最大连接数。缺省值:10;推荐的公式:((core_count * 2) + effective_spindle_count) -->18 <property name="maximumPoolSize" value="60" />19 <property name="minimumIdle" value="10" />20</bean>21 提示:如果想使创建的数据源参与Spring管理的事务,可以使用
TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy进行包装,但这并不推荐,操作数据库时最好是使用JdbcTemplate等更加抽象的API。
jdbc.properties配置
下面是jdbc.properties文件的常用配置:
421# HSQLDB 2#jdbc.driverClassName=org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver3#jdbc.url=jdbc:hsqldb:hsql://localhost:9001/bookstore4#jdbc.username=sa5#jdbc.password=6 7# MySQL 8jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver9jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test10jdbc.username=root11jdbc.password=root12 13# PostgreSQL 14#jdbc.driverClassName=org.postgresql.Driver15#jdbc.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost/bookstore16#jdbc.username=17#jdbc.password=18 19# Oracle 20#jdbc.driverClassName=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver21#jdbc.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl22#jdbc.username=scott23#jdbc.password=scott24 25# MS SQL Server 2000 (JTDS) 26#jdbc.driverClassName=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver27#jdbc.url=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://localhost:1433/bookstore28#jdbc.username=29#jdbc.password=30 31# MS SQL Server 2000 (Microsoft) 32#jdbc.driverClassName=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver33#jdbc.url=jdbc:sqlserver://192.168.1.130:1433;databaseName=test34#jdbc.username=35#jdbc.password=36 37# ODBC 38#jdbc.driverClassName=sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver39#jdbc.url=jdbc:odbc:bookstore40#jdbc.username=41#jdbc.password=42
4.2 初始化数据源
在容器启动时,如果需要对数据源进行初始化,可以使用org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.init包提供的数据源初始化功能。
161<!-- 初始化数据源dataSource2 enabled:根据环境变量来控制是否执行初始化3 separator:初始化脚本默认的语句分隔符。4 ignore-failures:忽略所有DROP语句错误。默认为NONE,可选的还有ALL-忽略所有错误。5-->6<jdbc:initialize-database 7 data-source="dataSource" 8 enabled="#{systemProperties.INITIALIZE_DATABASE} 9 separator="@@" 10 ignore-failures="DROPS">11 <!--初始化脚本1。指定脚本中语句的分隔符为";"-->12 <jdbc:script location="classpath:com/myapp/sql/db-schema.sql" separator=";"/>13 <!--初始化脚本2。以字典顺序执行所有匹配的脚本,使用默认的语句分隔符@@。-->14 <jdbc:script location="classpath:com/myapp/sql/db-test-data-*.sql"/>15</jdbc:initialize-database>16
注意:
如果您需要更精细的控制,可以直接使用
DataSourceInitializer并将其定义为应用程序中的组件。如果其它Bean在Spring容器启动过程中依赖数据源的初始化,则必须注意它们的先后顺序。
4.3 获取数据库连接
在Spring应用中,数据库连接一般通过DataSourceUtils来获取,这样可以参与到Spring管理的事务之中。DataSourceUtils类是一种方便且功能强大的工具类,它提供静态方法从数据源获取连接并在必要时关闭连接,常用的方法如下。
191// 获取连接。先尝试从事务线程上下文获取连接,如果获取失败,则调用数据源获取新连接。2// 如果事务同步处于活动状态,还会将新获得的连接绑定到线程上下文。3Connection getConnection(DataSource dataSource)4
5// 释放连接。如果事务同步处于活动状态,则归还到线程上下文,否则直接关闭连接。6void releaseConnection( Connection con, DataSource dataSource)7
8// 获得被包装的最原始连接9Connection getTargetConnection(Connection con)10
11// 判断连接是否为事务性连接,即通过Spring绑定到当前线程12boolean isConnectionTransactional(Connection con, DataSource dataSource)13
14// 修改JDBC语句的超时时间为指定的超时时间15void applyTimeout(Statement stmt, DataSource dataSource, int timeout)16
17// 修改JDBC语句的超时时间为事务设置的超时时间18void applyTransactionTimeout(Statement stmt, DataSource dataSource)19
注意:
Jdbctemplate等一些Spring提供的类获取连接也是通过DataSourceUtils来进行的。
代码中最好不要使用
jdbcTemplate.getDataSource().getConnection()的方式来获取连接,这个连接不是事务线程上下文绑定的连接,不参与Spring管理的事务,并且还必须手动调用close()方法去关闭它。如果处于事务上下文中,那么开发者不需要显示关闭或者释放连接,但是如果 DataSourceUtils 在没有事务上下文的方法中使用 getConnection() 获取连接,依然会造成数据连接泄漏,这个时候就需要显示release了。
第05章_快速测试
第一节 SpringTest简介
1. SpringTest是什么?
SpringTest可以方便的对Spring程序进行单元测试和集成测试,一般与Junit或TestNG等测试工具整合使用。
2. SpringTest整合Junit4
1) 引入相关依赖
181 <dependencies>2 <dependency>3 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>4 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>5 <version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version>6 </dependency>7 <dependency>8 <groupId>junit</groupId>9 <artifactId>junit</artifactId>10 <version>4.13.2</version>11 <scope>test</scope>12 </dependency>13 <dependency>14 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>15 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>16 <version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version>17 </dependency>18 </dependencies>
2) 编写业务类
71public class UserService {3 public void sayHello() {4 System.out.println("hello");;5 }6}7
3) 编写测试类
201package org.example.spring.test.service;2
3import org.junit.Test;4import org.junit.runner.RunWith;5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;6import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;7import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;8 9(SpringRunner.class) // 整合Junit4,也可以使用 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)10(classes = {UserService.class}) // 上下文配置11public class UserServiceTest {12 13 private UserService userService;14
15 16 public void testHello() {17 userService.sayHello();18 }19}20
3. SpringTest整合Junit5
1) 引入相关依赖
181 <dependencies>2 <dependency>3 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>4 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>5 <version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version>6 </dependency>7 <dependency>8 <groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>9 <artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>10 <version>5.5.2</version>11 <scope>test</scope>12 </dependency>13 <dependency>14 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>15 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>16 <version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version>17 </dependency>18 </dependencies>
2) 编写业务类
71public class UserService {3 public void sayHello() {4 System.out.println("hello");;5 }6}7
3) 编写测试类
221package org.example.spring.test.service;2
3import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;4import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;5import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;6import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;7import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;8import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig;9
10(SpringExtension.class) // 整合Junit511(classes = {UserService.class}) // 上下文配置12// @SpringJUnitConfig(classes = {UserService.class}) // 可以使用该注解替换上面两注解13public class UserServiceTest2 {14 15 private UserService userService;16
17 18 public void testHello() {19 userService.sayHello();20 }21}22
第二节 相关注解介绍
1. @ContextConfiguration
@ContextConfiguration用于指定ApplicationContext的配置信息,可以来自XML、Groovy、@Configuration类或Spring的其它组件等。
331package com.example;2
3(SpringRunner.class)4 // 从默认位置加载XML配置(如com.example.MyTest类加载classpath:com/example/MyTest-context.xml配置)5public class MyTest {6}7
8// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9
10(SpringRunner.class)11(locations={"/app-config.xml", "/test-config.xml"}) //从locations位置加载XML配置12public class MyTest {13}14
15// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------16
17(SpringRunner.class)18(classes = {AppConfig.class, TestConfig.class}) // 加载@Configuration类或组件类等(默认测试类的静态内部类加载)19public class MyTest {20}21
22// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
24(initializers = CustomContextIntializer.class) // 通过自定义上下文初始化器加载配置25public class ContextInitializerTests {26}27
28// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------29
30(locations = "/test-context.xml", loader = CustomContextLoader.class) // 通过自定义上下文加载器加载配置31public class CustomLoaderXmlApplicationContextTests {32}33
这些配置可以通过类继承的方式来继承和覆盖:
111(SpringRunner.class)2(classes = BaseConfig.class) // 加载基础配置3public class BaseTest {4 // class body...5}6
7(classes = ExtendedConfig.class) // 继承基础配置,并使用扩展配置覆盖8public class ExtendedTest extends BaseTest {9 // class body...10}11
2. @ActiveProfiles
@ActiveProfiles用于指定测试时激活的Profile。
51({"dev", "integration"}) // 激活dev和integration3public class DeveloperIntegrationTests {4}5
3. @TestPropertySource
@TestPropertySource用于配置测试属性文件和优先级更高的内联测试属性,并将其添加到Environment中的PropertySources集合中,以便为集成测试加载ApplicationContext。
81(3 locations = "/test.properties", // 从类路径下加载测试属性文件4 properties = {"timezone = GMT", "port: 4242"} // 配置内联测试属性,优先级比测试属性文件更高5)6public class MyIntegrationTests {7}8
提示:
@TestPropertySource配置的属性优先级高于OS环境变量、Java系统属性、@PropertySource属性以及编程方式添加的属性源加载的属性。
@TestPropertySource也支持通过类继承的方式进行继承和覆盖。
4. 事务相关注解
@Transaction:用于开启测试方法的事务支持,测试方法结束后默认回滚事务。
@Commit/@Rollback:用于标识测试方法进行提交或回滚,可作用于类或方法之上,默认进行回滚操作。
@BeforeTransaction/@AfterTransaction:用于标识方法在事务之前/事务之后执行。
341(SpringRunner.class)2(transactionManager = "txMgr")4public class FictitiousTransactionalTest {6
7 8 void verifyInitialDatabaseState() {9 // logic to verify the initial state before a transaction is started10 }11
12 13 public void setUpTestDataWithinTransaction() {14 // set up test data within the transaction15 }16
17 18 // overrides the class-level @Commit setting19 20 public void modifyDatabaseWithinTransaction() {21 // logic which uses the test data and modifies database state22 }23
24 25 public void tearDownWithinTransaction() {26 // execute "tear down" logic within the transaction27 }28
29 30 void verifyFinalDatabaseState() {31 // logic to verify the final state after transaction has rolled back32 }33
34}
5. @Sql/@SqlConfig/@SqlGroup
这三个注解用于在测试方法之前或之后执行一些SQL脚本,默认执行的脚本为类目录下的.sql文件,如com.example.MyTest类的默认脚本为classpath:com/example/MyTest.sql。
x1({ 3 (scripts = "/test-schema.sql", config = (commentPrefix = "`", separator = "@@")), // 执行/test-schema.sql脚本,并设置注释前缀和SQL语句分隔符。4 (5 scripts = "delete-test-data.sql",6 config = (transactionMode = ISOLATED), // 在隔离的事务中运行脚本7 executionPhase = AFTER_TEST_METHOD) // 在测试方法之后执行8 })9public void userTest {10 // execute code that uses the test schema and test data11}12
13
6. 其它不常用注解
@Timed:设置超时时间。
@Repeat:重复运行测试N次。
@BootstrapWith:用于指定自定义的TestContextBootstrapper。
@DirtiesContext:用于标识ApplicationContext是否被弄脏,当标记为脏时,会将其从测试框架的缓存中删除并关闭。
@TestExecutionListeners:用于配置TestExecutionListener,并向TestContextManager注册。
@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy:存在一些已知问题,推荐使用来自基础测试框架的测试生命周期回调。
@ContextHierarchy:用于定义ApplicationContext实例的层次结构以进行集成测试。
@WebAppConfiguration:用于声明ApplicationContext为WebApplicationContext类型,适用于测试Web应用程序,并从
file:src/main/webapp加载Web资源,创建MockServletContext。
第三节 其它补充知识
1. 常用测试工具
SpringTest包中提供了一些测试可能用到的工具类,如ReflectionTestUtils、AopTestUtils和JdbcTestUtils等,可参考相关官方文档。